Figure 2.
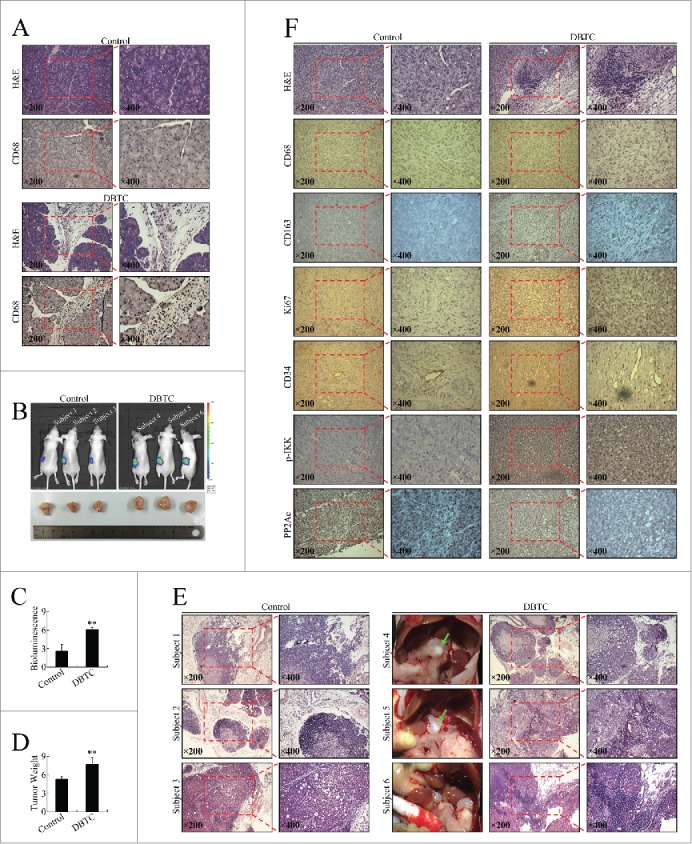
Inflammatory stimuli promoted pancreatic cancer cell growth and invasion in vivo. (A) Chronic inflammatory infiltration of leukocytes, fibroblast proliferation and fibrosis, large regions of acinar loss, and infiltration of CD68+ cells in the pancreas of DBTC-treated mice. (B) The effect of DBTC on pancreatic cancer in representative in vivo bioluminescent images and photographs of cancer xenografts. (C) Bioluminescence of pancreatic orthotopic xenografts. **P < 0.01 as compared to control. (D) Tumor weight of pancreatic orthotopic xenografts. **P < 0.01 as compared to control. (E) Pathological examination of metastatic cancerous nodes and celiac lymph nodes. Green arrow: metastatic cancerous node. (F) Pathological and immunohistochemical examination of pancreatic orthotopic xenografts. Immunohistochemistry was performed using antibodies targeting CD68, CD163, Ki67, CD34, p-IKK (phosphorylated IKK), and PP2Ac.
