Figure 1.
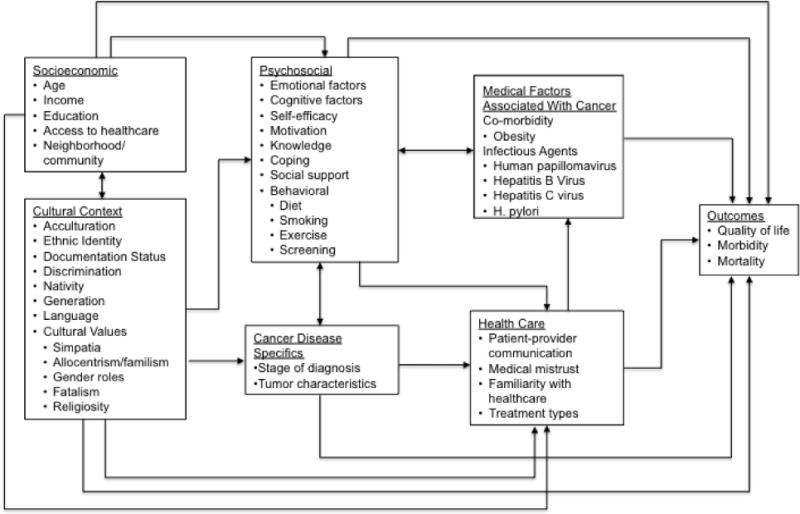
Conceptual model of determinants of cancer outcomes in Hispanics. Socioeconomic and cultural factors are interrelated and indirectly contribute to cancer outcomes through a series of modifiable factors such as psychosocial factors (e.g., coping, support, behaviors), cancer disease-specific factors (e.g., tumor characteristics), health care factors (e.g., cancer treatments, patient-physician communication), and medical factors associated with cancer (e.g., infectious agents and obesity).
