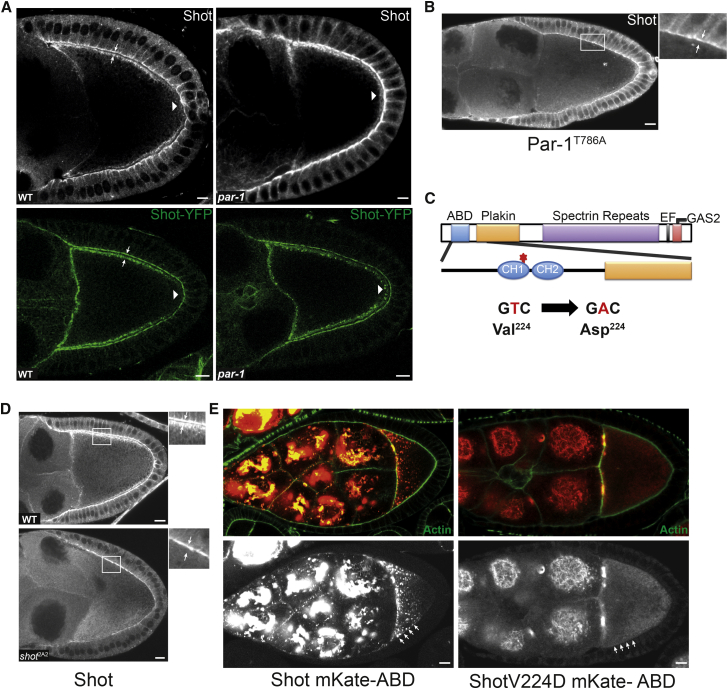
Figure 2.
The Cortical Localization of Shot Depends on Its Actin-Binding Domain and Is Inhibited by Par-1
(A) Shot localizes to the anterior-lateral cortex and is excluded from the oocyte posterior (left). Shot spreads around the oocyte posterior in the par-16323/par-1W3 mutant (right). Top: Shot antibody. Bottom: Shot-YFP genomic BAC.
(B) Overexpression of Par-1T786A-GFP displaces Shot from the oocyte cortex.
(C) Diagram of the domain structure of Shot, indicating the position and the nature of the point mutation in shot2A2. CH, calponin homology domain. CH1 and CH2 form the actin-binding domain (ABD).
(D) shot2A2 disrupts the localization of Shot to the oocyte cortex. The small boxes on the right are higher-magnification views showing the localization of Shot to the lateral cortex of the wild-type (WT) oocyte and its absence in shot2A4. Shot also localizes to the apical cortex of the follicle cells.
(E) Wild-type Shot ABD (left) localizes to the anterior-lateral cortex, whereas the Shot ABD with a Val224 to Asp mutation (right) does not.
Arrows point to the cortical Shot signal in the oocyte and to the underlying apical signal in the epithelial follicle cells (A, B, D). Arrowheads in (A) point to posterior. Arrows in (E) indicate the cortical signal. Scale bars represent 10 μm.