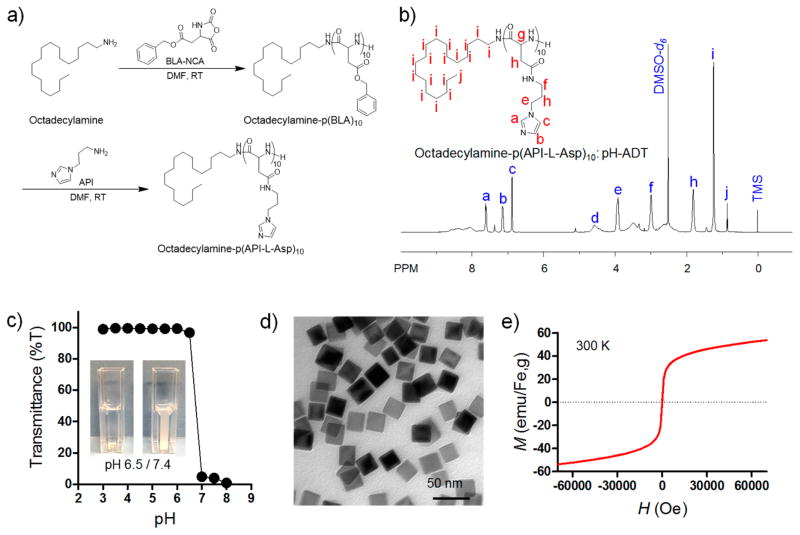
Figure 2.
Synthesis of pH-responsive additive (pH-ADT) and iron oxide nanocubes (IONCs) and their physicochemical characterization. (a) Chemical synthetic route for pH-ADT [octadecylamine–poly(API-L-Asp)10]. (b) 1H NMR analysis of pH-ADT in DMSO-d6. (c) Light transmittance of pH-ADT solution as a function of pH value. (Inset) Data for turbidity difference of pH-ADT solution at pH 6.5 (%T ≈ 97) and 7.4 (%T ≈ 4). (d) TEM image of iron oxide nanocubes (scale bar 50 nm). (e) Field-dependent magnetization curves of IONCs at 300 K.