Fig. 8.
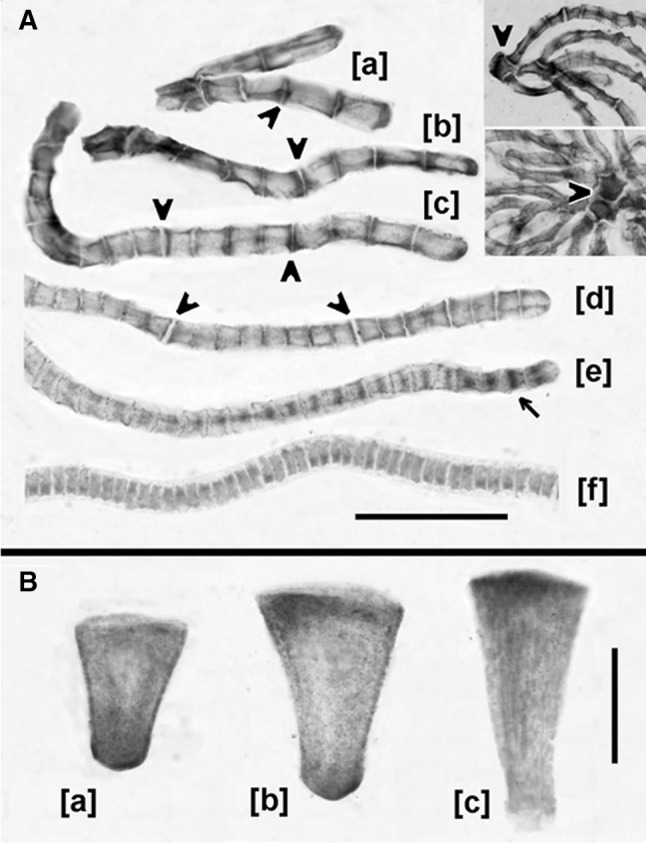
Immunohistochemical staining of antheridial cells of C. vulgaris using anti-IAA and AP-conjugated antibodies. a Antheridial filaments during successive developmental stages: [a] 2- and 4-celled filaments, [b, c] 8- and 16-celled filaments, respectively, [d, e] 32-celled filaments, [f] 64-celled filament; [e] an asynchronous filament composed of telophase cells showing immunolocalization of IAA to the phragmoplasts. Insertions presented at lower magnification in the upper right corner show antheridial filaments adjoined to the heavily stained capitular cells (arrowheads). Scale bar 30 μm for [a–f] and 50 μm for the insertions. b Localization of IAA in manubria varies depending on the developmental period of an antheridium. During the early stages of the proliferative period [a], IAA is asymmetrically distributed, close to the shorter wall of the manubrium connected with the complex of capitular cells; at later stages [b, c] polarization of IAA changes towards the longer transverse cell wall of the manubrium, which is adjoined to the shield cell. Scale bar 30 μm
