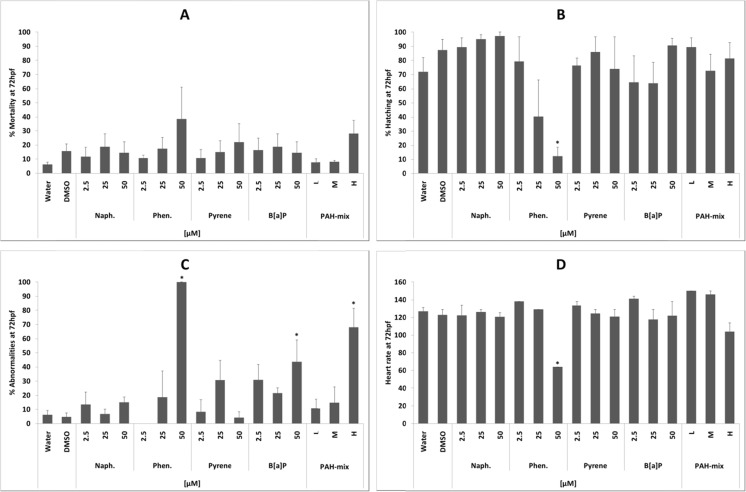
Fig. 2.
Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity of PAHs to zebrafish. Percent mortality (a), hatch rate (b), abnormalities (c) and heart rate (beats per minute (d)) at 72 hpf of exposure to increasing concentration of naphthalene, phenanthrene, pyrene and benzo[a]pyrene and a PAH mixture, as well as DMSO (0.05 % v/v) and untreated control. The exposure concentrations of individual compounds were 2.5, 25 and 50 μM. The concentrations for the PAH mixtures are set at low (L), medium (M) or high (H); see Table 1 for concentrations of individual PAHs within each mixture. Data are presented as average ± SE, and significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) to vehicle control are marked (*). Where error bars are not visible, the number of animals alive or affected between repeats was the same or similar