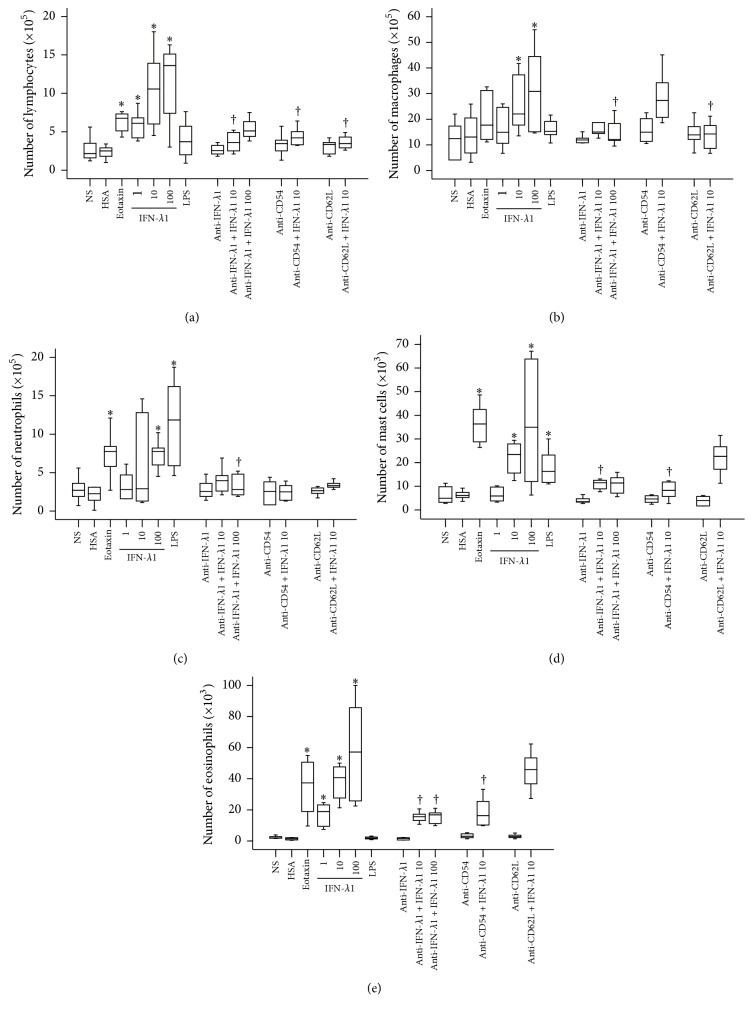
Figure 6.
Interferon- (IFN-) λ1 induces inflammatory cell accumulation in mouse peritoneum. Mice were treated with IFN-λ1 (ng/mL) in the presence or absence of its specific antibody (3.0 μg/mL), eotaxin (10 ng/mL), human serum albumin (HSA, 10 ng/mL), lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1.0 μg/mL), and normal saline (NS) for 6 h before their peritoneal lavage being collected for differential cell analysis. For certain mice, anti-CD54 antibody (anti-CD54, 1 mg·kg−1) and anti-CD62L antibody (anti-CD62L, 1 mg·kg−1) were injected via tail vein 30 min before IFN-λ1 being injected. Data were displayed as a boxplot, which indicates the median, interquartile range, the largest, and smallest values other than outliers (whiskers) and the outliers (O). Each piece of data represented a group of 6-7 animals. ∗ P < 0.05 compared with the corresponding NS group. † P < 0.05 compared with the corresponding stimulus alone group.