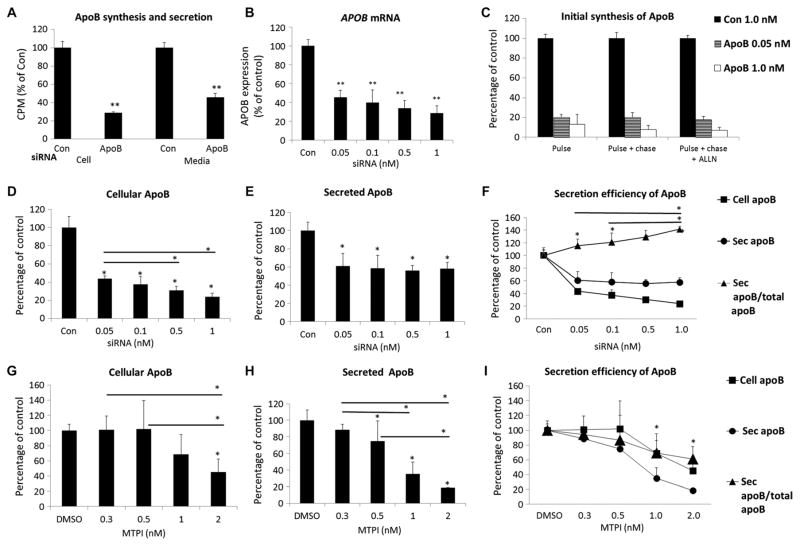
Fig. 2. Effects of siRNA-mediated knockdown of APOB on apoB secretion in human HepG2 cells.
(A) APOB siRNA (10 nM) inhibits the synthesis and secretion of apoB in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were transfected with 10 nM APOB or 10 nM irrelevant control (Con) siRNA for 2 days, radiolabeled continuously with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 2 hours, and radioactivity [counts per minute (CPM)] in cellular or media apoB was determined. (B) APOB siRNA knocks down APOB mRNA in a dose-dependent manner. HepG2 cells were transfected at varying doses of APOB siRNA for 2 days. Total RNA was extracted and APOB mRNA levels were analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). (C) APOB siRNA reduces initial synthesis rates of apoB in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were labeled with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 10 min and chased for 10 min with or without proteasome inhibitor ALLN pretreatment for 1 hour. (D and E) The effect of APOB siRNA doses on cellular and secreted apoB in HepG2 cells transfected as in (B), and apoB synthesis and secretion analyzed as in (A). (F) Efficiency of apoB secretion as a function of APOB siRNA knockdown. Efficiency was defined as the percentage of apoB secreted into the medium compared with the amount of total newly synthesized apoB (cellular and secreted apoB over 2 hours). (G and H) Cellular and secreted apoB in HepG2 cell culture after treatment with an MTP inhibitor (MTPI) for 1 hour (before steady-state labeling for 2 hours). (I) Efficiency of apoB secretion as a function of MTP inhibition. Data were plotted using the cell and secreted apoB data, as described in (F). All data are mean percentage of control [siRNA (1 nM) in (B) to (F); dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in (G) to (I)] ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus respective control, unless otherwise noted, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc comparisons using the Fisher LSD (least significant difference) method.