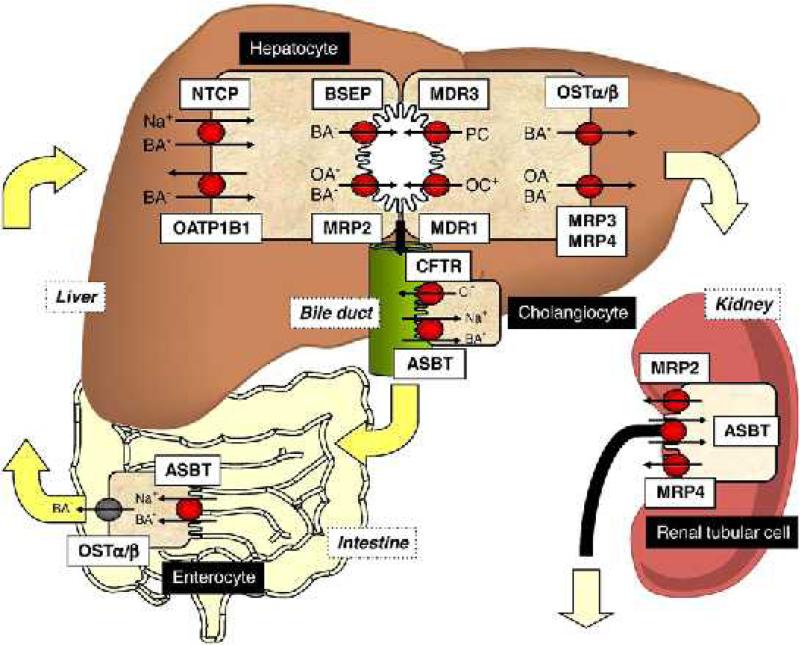
Figure 1.
Bile acid transporters in the hepatobilliary system, intestine and kidney (74). Bile acids are transported from portal blood into hepatocytes by NTCP and OATP. They are effluxed at the canalicular membrane by BSEP and MRP2. MRP3, MRP4 and OSTalpha/beta efflux bile acids at the basolateral membrane back to the systemic circulation. MDR3 transports phospholipids and MDR1 transports cations including drugs across the apical membrane. Bile acid reabsorption can occur at the level of the cholangiocyte, via ASBT, the terminal ileum via ASBT and within the enterocyte, bile acids are effluxed by OSTalpha/beta. Bile acids can also be reabsorbed in the proximal renal tubule via ASBT. Bile acids may be excreted into urine via MRP2 and MRP4. Reproduced with permission from (74).