FIG 4.
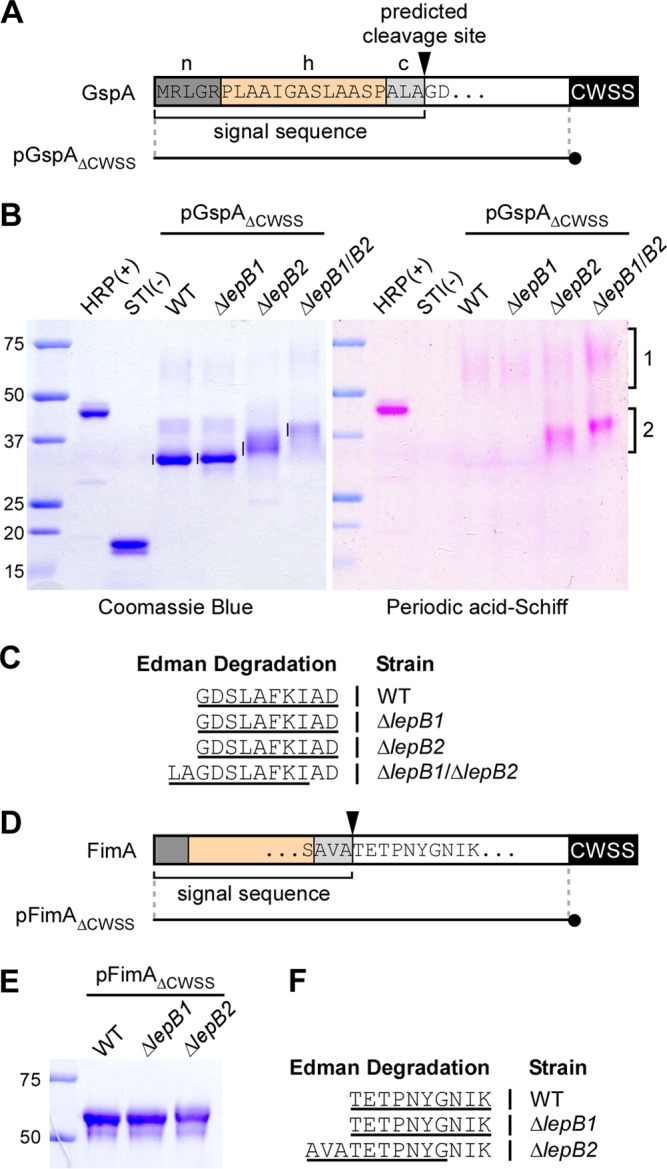
Mapping of the signal peptide cleavage site by Edman degradation. (A) Shown is a graphic representation of GspA. The N-terminal sequence of GspA contains a typical signal peptide composed of a positively charged polar region (n), a hydrophobic central region (h), and a region with the SPase recognition motif AXA (c). The arrowhead marks the predicted SPase I cleavage site. pGpsAΔCWSS is a plasmid expressing a GspA variant in which the CWSS is replaced with a 6-His tag (black circle). (B) His-tagged GspA proteins from the culture medium of the strains indicated were purified by affinity chromatography, separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by Coomassie blue (∼1.25 μg of proteins in all lanes) and PAS (2.5 μg of proteins) staining. Glycosylated HRP and nonglycosylated soybean trypsin inhibitor (STI) were used as positive and negative controls. Numbered brackets indicate glycosylated forms of GspA. (C) The bands indicated by vertical lines in panel B were subjected to Edman degradation. The N-terminal sequence of GspA was deduced from the first 10 sequencing cycles (underlined). Samples from the ΔlepB1 ΔlepB2 double mutant produced ragged N-terminal sequencing with the major sequence shown. (D) Like GspA, FimA harbors a signal peptide with the conserved cleavage site motif AXA. pFimAΔCWSS is a plasmid expressing a FimA molecule in which the CWSS is replaced with a 6-His tag (black circle). (E) His-tagged FimA proteins from the culture medium of the strains indicated were purified by affinity chromatography, separated by SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie blue. (F) The purified proteins were subjected to N-terminal sequencing. The sequences that resulted from first 10 sequencing cycles are underlined. The lepB2 mutant also produced ragged N-terminal sequencing with the major sequence shown. The values to the left of panels B and E are molecular sizes in kilodaltons.
