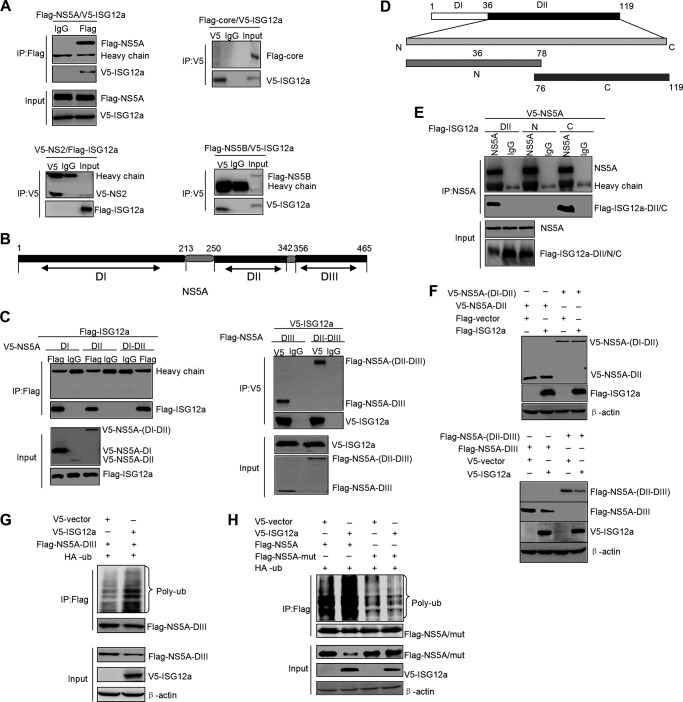
FIG 4.
ISG12a interacts with NS5A. (A) IP analysis of ISG12a and viral protein from HEK293T cells expressing exogenous ISG12a and individual viral proteins, including NS5A, core, NS2, and NS5B. (B) Schematic representation of the domains of NS5A. (C) IP analysis of ISG12a and various domains of NS5A from HEK293T cells expressing exogenous ISG12a and different domains of NS5A, including NS5A DI, DII, DI-DII, DIII, and DII-DIII. (D) Schematic representation of the domains of ISG12a. (E) IP analysis of NS5A and various domains of ISG12a from HEK293T cells expressing exogenous NS5A and different domains of ISG12a, including ISG12a DII, DII-N, and DII-C. (F) Western blotting of lysates from HEK293T cells expressing exogenous ISG12a and different domains of NS5A for 48 h. (G) Ubiquitination assay and Western blotting of lysates from HEK293T cells cotransfected with the indicated plasmids for 48 h. MG132 (25 μM) was added to cells for 6 h prior to harvesting of cell lysates, and IP experiments were conducted with anti-Flag antibody followed by the ubiquitination assay of NS5A DIII protein. (H) Cells were treated as described for panel G, followed by the ubiquitination assay of wild-type or K374R mutant NS5A protein. V5, Flag, and HA were the tags used.