Figure 2.
Cell Division Is a Key Process Associated with Induced Phloem Cells.
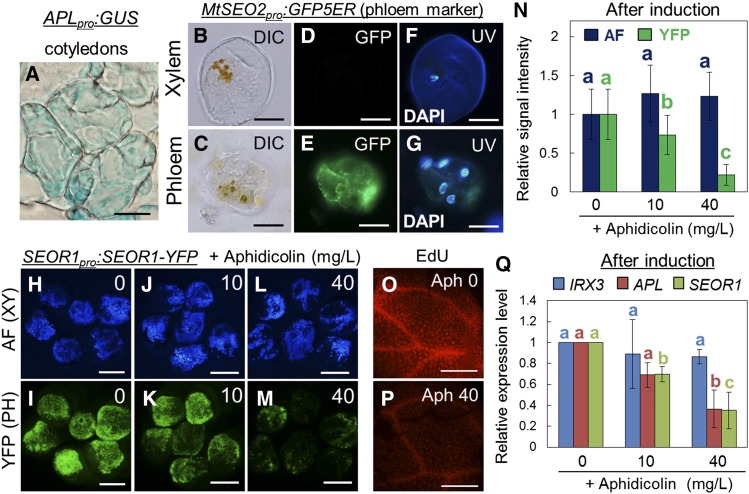
(A) Cross-section image of APLpro:GUS cotyledons cultured for 4 d.
(B) to (G) Fluorescence images from DAPI staining and phloem marker (MtSEO2pro:GFP5ER) expression in an isolated immature xylem lump ([B], [D], and [F]) and an isolated phloem lump ([C], [E], and [G]). Differential interference contrast (DIC) images ([B] and [C]), GFP fluorescence images ([D] and [E]), and DAPI staining images ([F] and [G]) were obtained 3 d after induction in VISUAL.
(H) to (M) Effects of aphidicolin on autofluorescence (AF) of xylem secondary cell wall and YFP signal of SEOR1pro:SEOR1-YFP. Aphidicolin (0, 10, and 40 mg/L) was added to the culture medium at 24 h after the start of preculture (see also Supplemental Figure 2).
(N) Quantification of fluorescence signal intensities for (H) to (M). Relative signal intensity was calculated by comparison to a sample cultured without aphidicolin. Error bars indicate sd (n = 12; number of analyzed cotyledons). Significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters (Tukey’s test).
(O) and (P) Effects of aphidicolin on cell division in VISUAL. DNA replication in VISUAL was detected by labeling with the modified thymidine analog EdU after no (O) or 40 mg/L aphidicolin treatment (P). EdU accumulation is indicated by red fluorescent signals.
(Q) Effects of aphidicolin on expression levels of xylem- (IRX3) and phloem-related (APL and SEOR1) genes. Relative expression levels were calculated by comparison to a sample cultured without aphidicolin. Error bars indicate sd (n = 3; biological replicates). Significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters (Tukey’s test).
Bars = 50 μm in (A), 20 μm in (B) to (G), 2 mm in (H) to (M), and 500 μm in (O) and (P).