Figure 2.
Localization of GFP-CKL2 Expressed from the Native CKL2 Promoter.
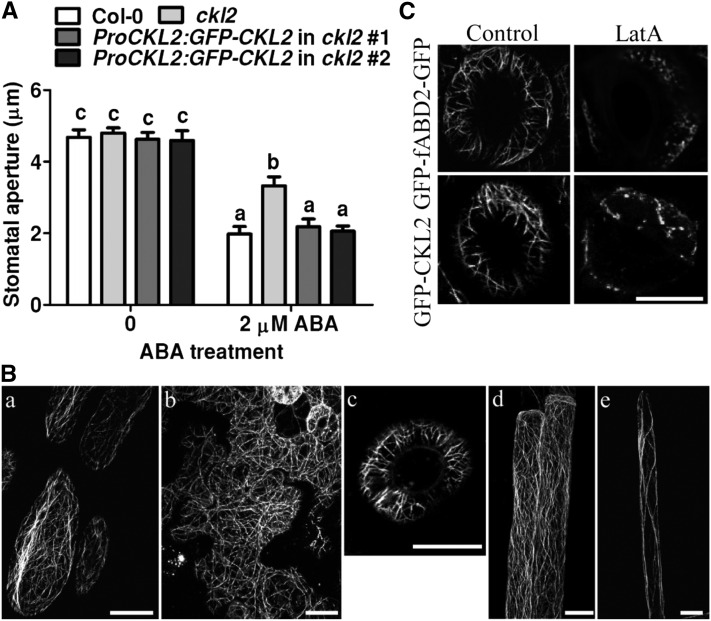
(A) Stomatal bioassays for ABA-induced closure in Col-0, ckl2, and two ProCKL2:GFP-CKL2 transgenic lines. The data represent the means ± sd of three independent experiments; 50 stomata were analyzed per line. The data sets were tested for normal distribution by the Shapiro-Wilk test. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test; significant differences are indicated by different lowercase letters. The t test analysis of the data indicated the levels of significance to be P = 0.0024, 0.8673, and 0.8358 for ckl2 and two rescued lines data, respectively, compared with Col-0 after ABA treatment. Before ABA treatment, the levels of significance were P = 0.9023, 0.3251, and 0.6601 for ckl2 and two rescued lines, respectively, compared with Col-0.
(B) Confocal images were taken of epidermal cells of hypocotyls (A), leaves (B), guard cells (C), roots (D), and root hairs (E) of ProCKL2:GFP-CKL2 transgenic seedlings in the Col-0 background. Bars = 10 μm.
(C) GFP-CKL2 driven by the CKL2 native promoter and GFP-fABD2-GFP transgenic seedlings were treated with 200 nM LatA for 0.5 h. Confocal images were taken of guard cells. Bars = 10 μm.