Figure 6.
Phosphorylation of ADF4 by CKL2 Affects ADF4 Activity.
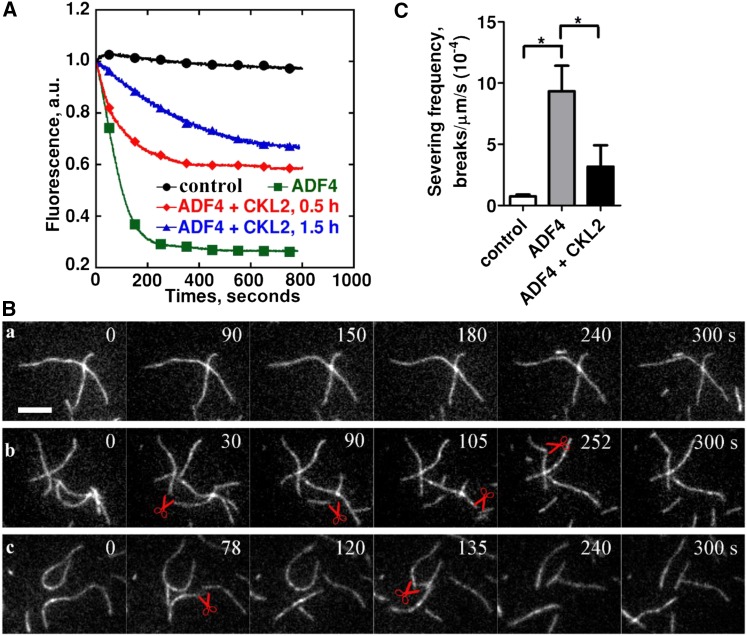
(A) The effect of ADF4 on F-actin disassembly was determined by a pyrene-actin assay. ADF4, after being phosphorylated by CKL2, was able to depolymerize actin filaments but was less potent than nonphosphorylated ADF4. Preassembled actin filaments (from 2 µM G-actin, 10% pyrene-labeled) were incubated with 250 nM ADF4 or 250 nM CKL2-phosphorylated ADF4 to induce actin disassembly at pH 7.0. Black closed circles, 0.5 µM F-actin; green closed squares, 0.5 µM F-actin + 4 µM ADF4; red closed diamonds, 0.5 µM F-actin + 4 µM ADF4 after phosphorylation by CKL2 for 0.5 h; blue closed triangles, 0.5 µM F-actin + 4 µM ADF4 after phosphorylation by CKL2 for 1.5 h. a.u., arbitrary units.
(B) Time-lapse TIRF microscopy analysis of actin filament severing by ADF4 after being phosphorylated by CKL2. Time-lapse images were recorded at 3-s intervals with TIRF microscopy. Actin filaments (from 1 µM G-actin, 50% Oregon-green labeled) were monitored for 300 s without ADF4 (A), in the presence of 500 nM nonphosphorylated ADF4 (B) or 500 nM CKL2-phosphorylated ADF4 (C). The red pairs of scissors indicate severing events. See Supplemental Movie 3 for the entire series.
(C) Quantification of ADF4-mediated actin-filament-severing frequency. Averages for each condition are from at least 30 individual filaments obtained from three independent trials. Error bars represent means ± sd (n = 3). Statistical significance (*P < 0.5) was determined by Student’s t test. The t test analysis of the data indicated the level of significance to be P = 0.0186 and 0.1380 for ADF4 and ADF4 + CKL2 data relative to the control data, respectively. The level of significance between ADF4 and ADF4 + CKL2 data was P = 0.0219.