Fig. 2.
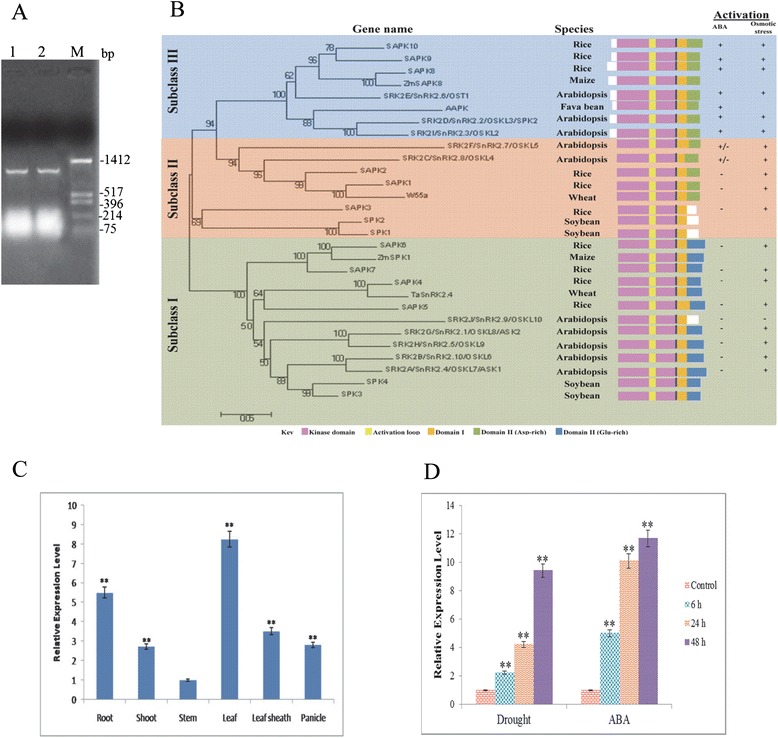
Analyses of phylogenetic relationship and tissue-specific expression of SAPK9 gene cloned from the wild rice O. rufipogon. a Agarose gel showing the RT-PCR amplification of SAPK9 coding DNA sequence (CDS) from drought-tolerant O. rufipogon. Lane 1-2 PCR product, Lane M- molecular marker. b Phylogenetic tree of SnRK2 family proteins from selected plant species. The phylogenetic tree was constructed in MEGA6.0 software with the neighbor-joining method. The numbers indicate the bootstrap values (1000 replications). c Analysis of real-time PCR depicting SAPK9 transcript expression in root, shoot, leaf, leaf sheath and panicle in O. Rufipogon. d Real-time PCR analysis of the SAPK9 transcript in leaf samples of O. rufipogon under dehydration and exogenous ABA (100 μM) treatment at 6, 24 and 48 h. Untreated 0 h sample in each cases were used as control. For internal reference, rice OsUbi1 gene was used. Error bars represent the mean ± SD of triplicate measurements. Student’s t-test was performed to find out statistically significant differences (**P < 0.01)
