Figure 2. mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice display an age-related longitudinal decline memory retention in the water maze.
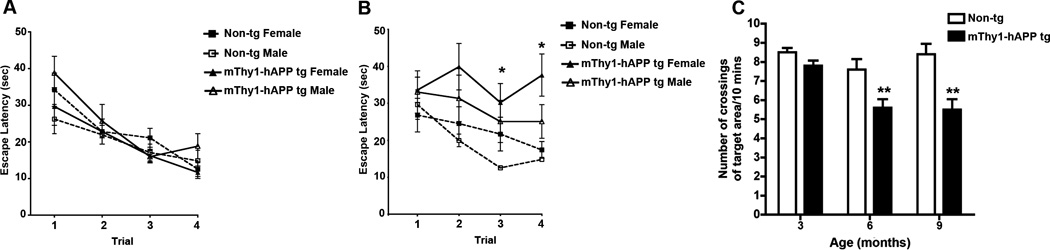
A) Relearning ability of non-Tg and mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice at 6 months of age on the retest days (four trials in which the platform was in the same position it had been on the final day of testing at 3 months). B) Relearning ability of non-Tg and mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice at 9 months of age on the retest days (four trials in which the platform was in the same position it had been on the final day of testing at 6 months). C) Retention abilities of non-Tg and mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice in the water maze indicated by the number of target crossing in the probe trials. Data are represented by means ± SEM. * Indicates significant difference between female and male mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice with p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA; ** Indicates significant difference between non-Tg and mThy1-hAβPP751 Tg mice with p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA.
