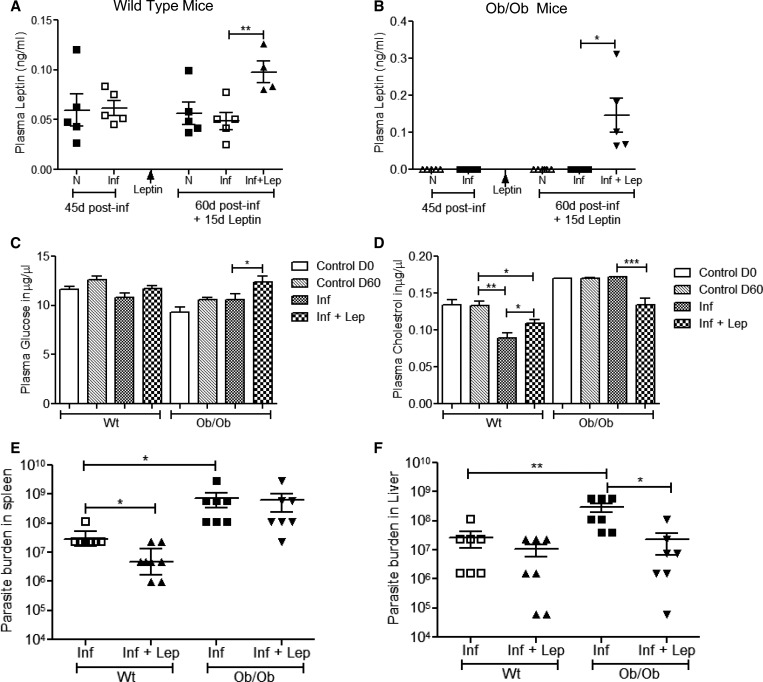
Figure 1.
Effect of exogenous leptin administration on plasma leptin, glucose, cholesterol levels, splenic, and liver parasite burden in normal and Ob/Ob mice. On day 0, mice were infected with Leishmania donovani by intravenous injection. On day 45 postinfection, leptin delivery pump was implanted in one group of infected mice; 15 days post leptin treatment, mice were euthanized. (A) Plasma leptin level of normal mice and (B) Ob/Ob mice was measured; naive mice (N), L. donovani infected (Inf), and L. donovani infected along with leptin treatment (Inf + Lep) at different times postinfection. (C) Plasma glucose and (D) cholesterol were measured as described in section Materials and Methods. Four to six mice were used in each group, and the experiments were repeated twice. (E) Parasite burden from the spleen and (F) the liver of different groups of mice at 60 days postinfection was measured and expressed as the geometric mean number of parasites per spleen and liver. Cumulative data of two independent experiments are shown (N = 7). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.005.