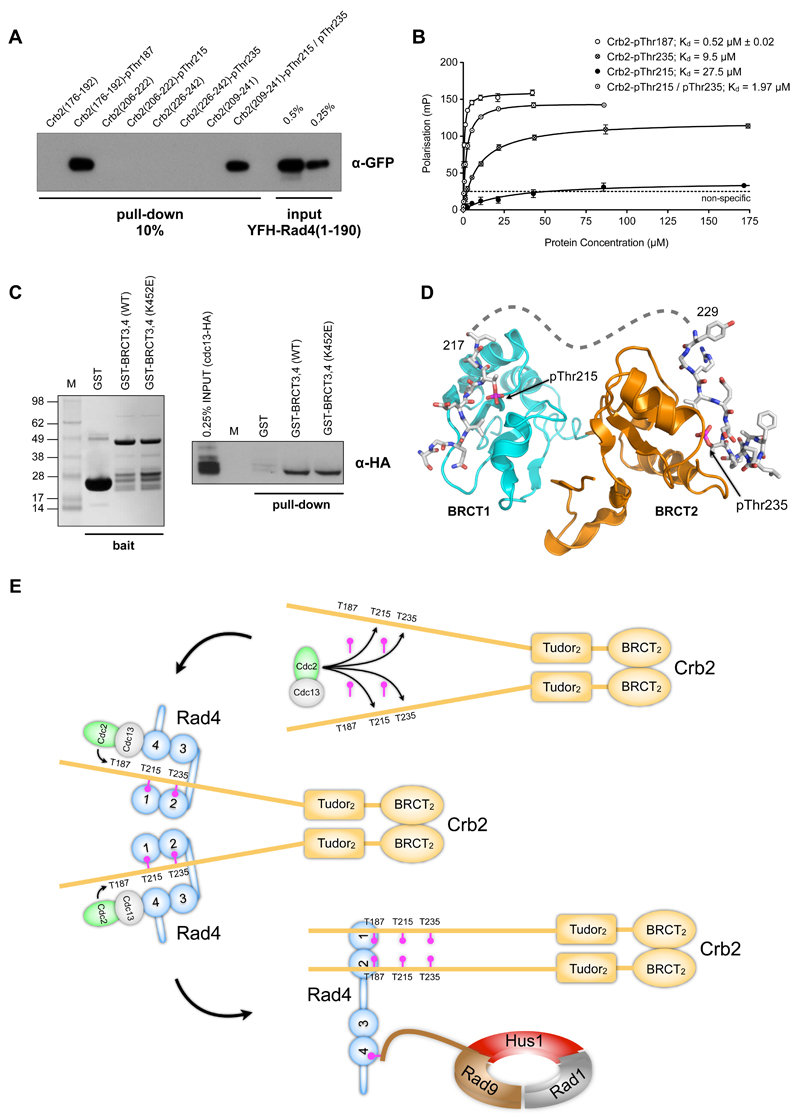
Figure 7. Hierarchical phosphorylation and checkpoint complex assembly.
A) A GFP-tagged Rad4 construct is efficiently co-precipitated by Crb2-derived peptides incorporating either pThr187, or bis-phosphorylated on pThr215 and pThr235, but not by unphosphorylated peptides or peptides with singly phosphorylated Thr215 or Thr235.
B) Phosphorylation of both Thr215 and Thr235 substantially increases the affinity of Crb2 peptides for Rad4-BRCT1,2 compared with those phosphorylated in isolation. The measured affinity (1.97 micromolar) is comparable to that for peptides incorporating pThr187. Data points are averages of three measurements; error bars indicate one standard deviation.
C) HA-tagged cyclin Cdc13 can be co-precipitated from S.pombe lysates by GST-Rad4-BRCT3,4, and GST-Rad4-BRCT3,4(K452E) containing a charge-reversal mutation in the phosphate-binding site of BRCT4, but not by GST alone.
D) Model of bi-dentate interaction of Crb2 segment phosphorylated on both Thr215 and Thr235. The perpendicular orientation of the BRCT domains allows pThr215 to bind to BRCT1 and pThr235 to BRCT2 with the intervening 12 amino acids connecting comfortably between the two.
E) Mechanism of hierarchical phosphorylation – (top) Cdc2-Cdc13 phosphorylates the canonical CDK target sites Thr215 and Thr235 in Crb2 in a cell-cycle dependent manner; (middle) Phosphorylation on Thr215 and Thr235 enables binding of Rad4 to Crb2, which in turn recruits Cdc2-Cdc13 via a phosphorylation-independent interaction with BRCT3,4 of Rad4. The ‘scaffold’ effect provided by simultaneous interaction of Rad4 with the CDK complex and its substrate, facilitates phosphorylation of the non-canonical site Thr187; (bottom) A single Rad4 is able to bind simultaneously to both pThr187 sites in a Crb2 dimer via BRCT domains 1 and 2, bridging Crb2 to the Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 complex via interaction of the phosphorylated C-terminus of Rad9 with BRCT4 of Rad4.