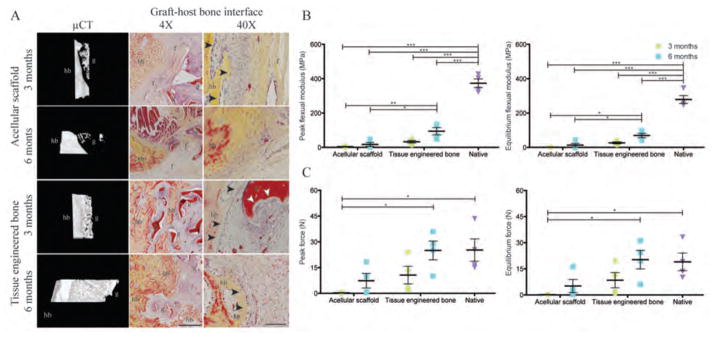
Figure 5. Graft-host bone integration.
(A) μCT 3D reconstruction of the graft-host interface and Movat’s pentachrome staining were used to assess integration of the implanted graft with the host bone. For acellular grafts, the mineralized host bone (hb) and the graft structures (g) were separated by soft fibrous tissue (f). In contrast, host bone (hb) extended into the tissue-engineered bone graft (g). In the proximity of the new bone, osteoclastic resorption (white arrowheads) was detected on the implanted scaffold with the lining of osteoblasts (black arrowheads), indicating active ossification. Scale bars: 1 mm (4×) and 100 μm (40×). (B and C) Three-point bending mechanical test for peak and equilibrium flexural moduli (B) and the peak and equilibrium forces (C). Data are means ± SD (n=4 from 2 animals for condylectomy; n=4 from 2 animals for 3 months data; n=8 from 4 animals for 6 month data). ***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05, two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc tests.