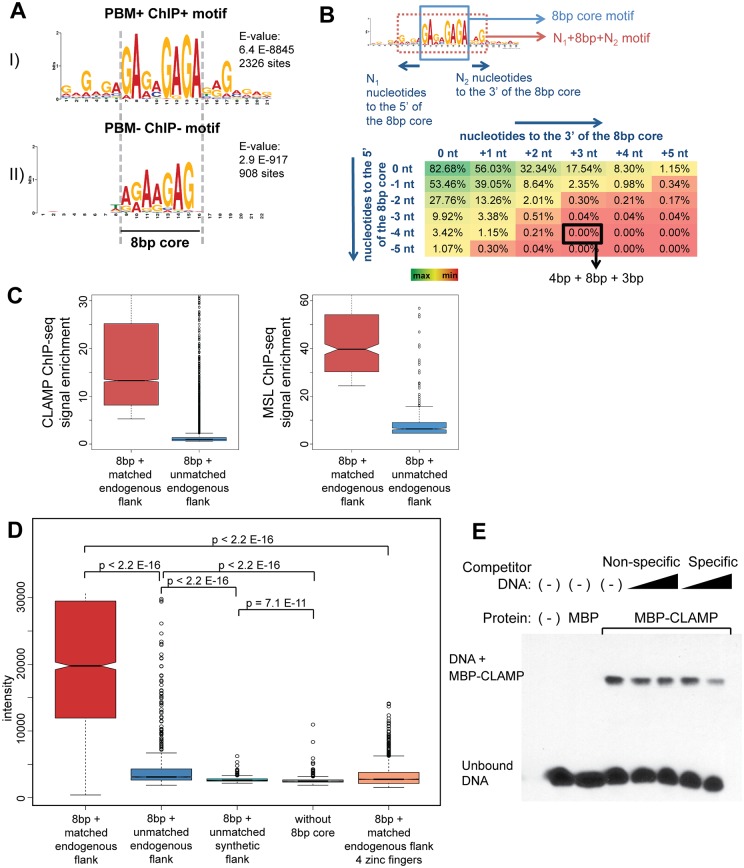
Fig 2. A long 15-bp motif increases CLAMP binding to DNA.
A) Motifs obtained from the custom gcPBMs are shown: I) The PBM+ChIP+ motif represents the sequences that CLAMP binds both in vivo and in vitro. II) The PBM-ChIP- motif represents the sequences that are on the array but not bound by CLAMP in vivo or in vitro. The most conserved 8-bp core element is indicated by vertical dashed lines. B) A representation of the methodology to define the minimal CLAMP-bound motif by scanning both 5’ and 3’ of the core motif. The table shows the percentage of PBM+ChIP+ (CLAMP binding both in vitro and in vivo) sequences that overlap with PBM-ChIP- sequences (CLAMP binding neither in vitro nor in vivo) at the specified motif size. The y-axis shows the nucleotides 5’ of the 8-bp core motif and the x-axis shows the nucleotides 3’. The scale ranges from green for the maximal values to red for the minimal values. Values show the percentage of PBM+ChIP+ sequences shared with PBM-ChIP- sequences for the length window selected. A value of zero overlapping sequences represents complete separation between PBM+ChIP+ and PBM-ChIP- sequences and is obtained at 4-bp 5’ and 3-bp 3’ of the core motif. C) CLAMP and MSL ChIP-seq enrichments are shown for sequences containing the 8-bp core with and without additional flanking sequence matching the motif. Motif hits were found using the FIMO tool (p < E-4). All 8-bp core hits were found first and the ones overlapping with the full 15-bp motif were separated as ‘8bp + matched endogenous flank’ and the rest were grouped as ‘8bp + unmatched endogenous flank’. Since the ‘8bp + unmatched endogenous flank’ group has ~10,000 sites, the top 10,000 enrichments are shown in the CLAMP enrichment plot. Since there are ~300 CES, the top 300 enrichments are shown in the MSL enrichment plot. D) Binding intensities are shown for the following classes of probes: 1) probes with the optimal motif (8-bp + matched endogenous flank, red); 2) probes that have matching 8-bp core regions but the endogenous flanks do not match the motif (8-bp + unmatched endogenous flanks, blue); 3) probes that have 8-bp cores with synthetic constant flanking sequences (8-bp + unmatched synthetic flank, cyan); 4) probes that do not have the 8-bp core motif (without 8-bp, brown); 5) Intensities for C-terminal 4 zinc finger GST fusion proteins are shown for probes containing the 15-bp CLAMP motif (15–bp, 4ZF, orange). E) CLAMP binds to DNA containing a high affinity, 8 bp + matched flank motif in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Biotin-labeled DNA alone (lane 1) and DNA with MBP (lane 2) do not shift, while MBP-CLAMP forms a complex with DNA to shift the signal. This was competed away with specific (high affinity) competitor but not a non-specific competitor that contains the 8-bp core but lacks endogenous flanking sequences (8-bp + unmatched synthetic flank).