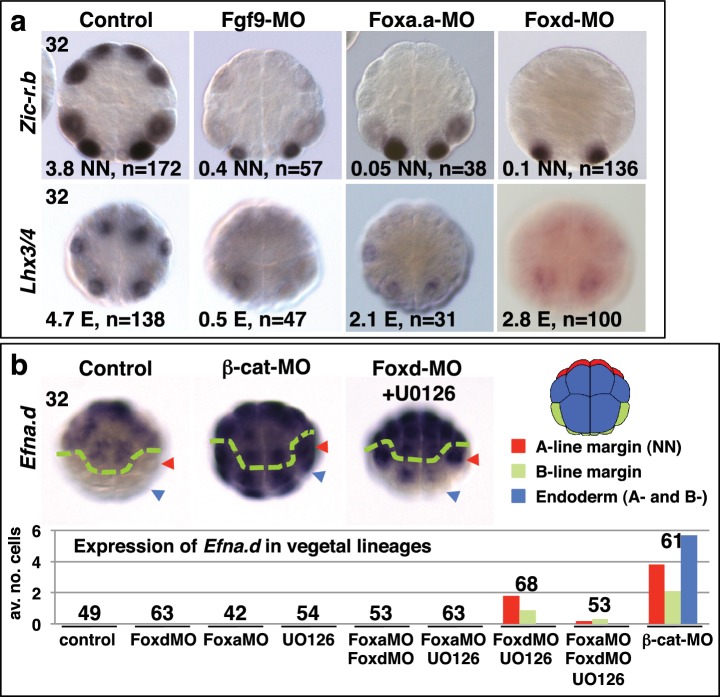
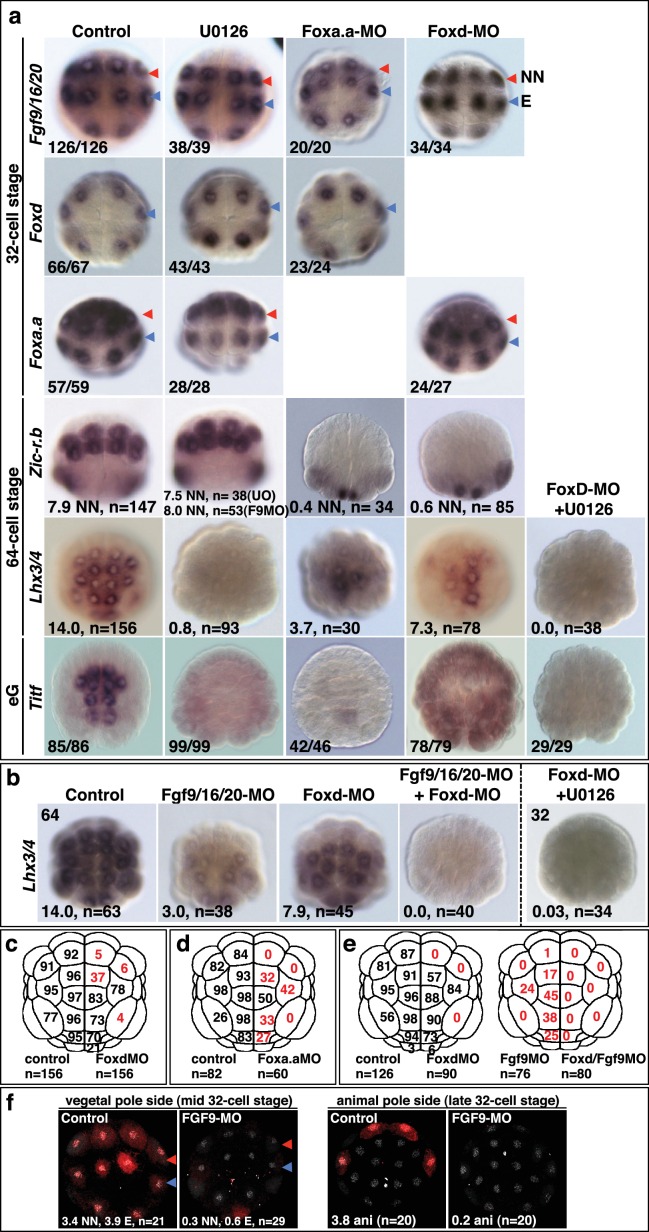
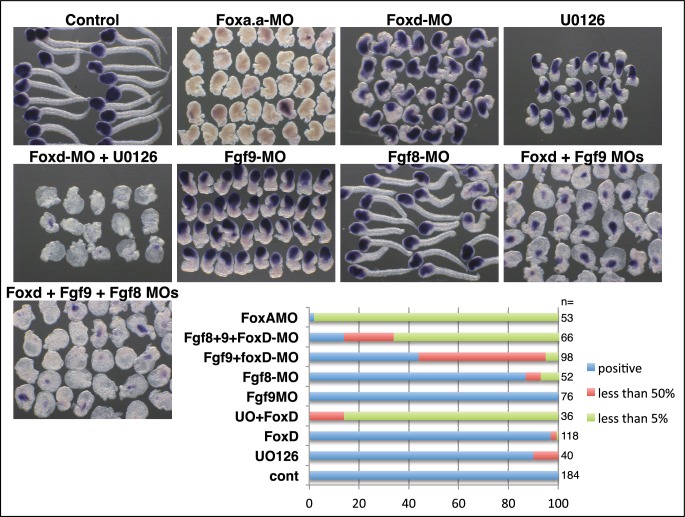
Figure 2. Foxa.a, Foxd and Fgf9/16/20 are required for initiation of NN and E gene expression.
(a) Embryos analysed at the 32-cell stage. The marker analysed is indicated on the left of the panels and the treatment indicated above the panels. The average number of NN (Zic-r.b) or E (Lhx3/4) cells expressing detectable levels of each gene is indicated. This remaining expression was generally weaker than control level expression. ‘n=’ represents the number of embryos analysed. (b) Expression of Efna.d under the conditions indicated. Embryos are shown in notochord-side view, animal pole up. The graph shows the average number of cells expressing Efna.d in different vegetal lineages at the 32-cell stage, as indicated by the key. All embryos showed ectoderm expression. The number of embryos analysed is indicated above the bars on the graph.