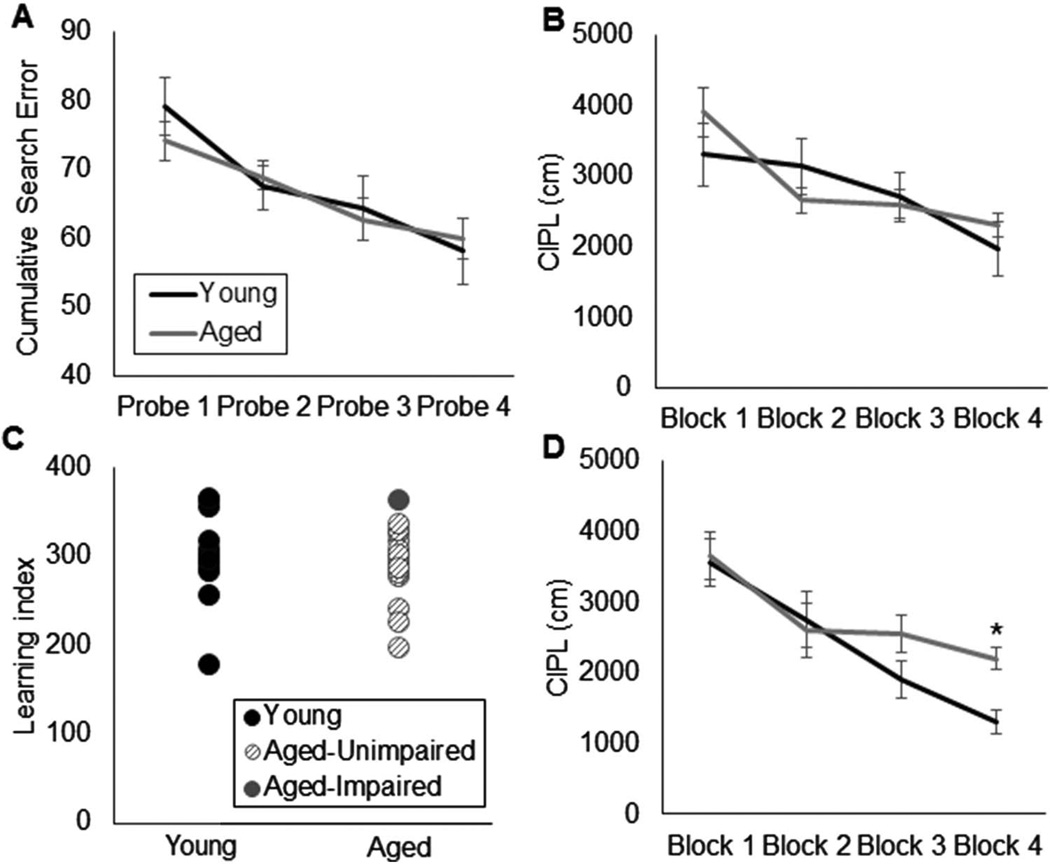
Figure 5.
Morris water maze test of spatial reference memory. (A) Cumulative search error (Y-axis) across all probe trials (X-axis) in young (black) and aged rats (gray). Cumulative search error during the 4 probe trials did not differ significantly between age group, F(1,28) = 0.16, p= .69, and all rats showed significantly reduced search errors after training, F(3,84) = 19.03, p< .001; repeated-measures. (B) Mean corrected integrated path length (CIPL) values (Y-axis) for young (black) and (aged) rats across training blocks (X-axis). CIPL values decreased as a function of training block, F(3,84) = 17.44, p< .001 (repeated-measures), which did not differ significantly with age, F(1,28) = 0.64, p= .43. (C) Individual Spatial Learning Index values (Y-axis) for young and aged rats calculated from the cumulative search error on probe Trials 2–4. Learning index also did not significantly differ between age group, F(1,28) = 0.34, p= .56. Moreover, only one aged rat performed outside of the normative range of the young group (impaired, solid circle). (D) CIPL values (Y-axis) for a different cohort of young (black) and (aged) rats across training blocks (X-axis). In this group of rats, which were not tested on the OPPA task, there was a significant effect of age on CIPL values during training Block 4 (T(24)= 2.99, p< .01). Error bars show +/−1 standard error of the mean.