Figure 11. Possible mechanism for glycogen phosphorylation.
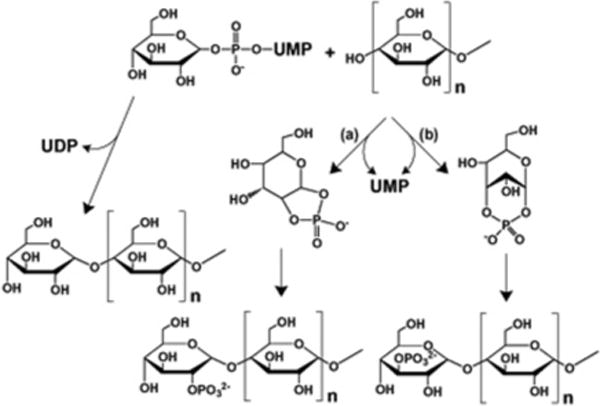
The usual glycogen synthase reaction is shown on the left where glucose from UDP-glucose is added to the non-reducing end to form a new α-1,4-glycosidic linkage. The proposed mechanism for the introduction of phosphate would involve the formation of either glucose-1,2-cyclic phosphate (a) or glucose-1,3-cyclic phosphate (b) in the enzyme active site. Reaction of C-1 of the cyclic phosphate would lead to addition of either a glucose 2-phosphate or a glucose 3-phosphate to the non-reducing end.
