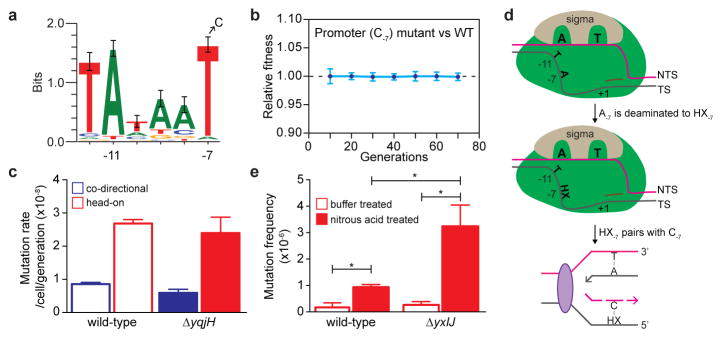
Figure 4. Promoter T-7→C-7 is a mutation hotspot generated via deamination.
a, The consensus −10 element of B. subtilis SigA-dependent promoters (n=358). The strongly conserved T-7 is frequently mutated to a C. b, Fitness of head-on T-7→C-7 mutant relative to head-on wild-type thyP3 cells under induced transcription (mean±s.d). c, Mutation rate of T-7→C-7 in yqjH mutant (error-prone polymerase PolIV). d, Model illustrating the mechanism of generation of T-7→C-7. During transcription initiation, the −10 element is single-stranded, creating solvent accessibility for A-7 on the template strand (TS), allowing it to be deaminated to hypoxanthine (HX). HX basepairs with C during replication, resulting in T-7→C-7. e, T-7→C-7 frequencies in head-on thyP3 upon nitrous acid treatment of wild-type and ΔyxlJ (hypoxanthine-DNA glycosylase) strains. (*-P<0.05; Student’s t-test).