Figure 1.
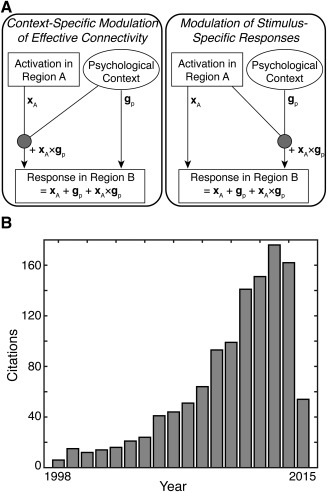
Overview of Psychophysiological Interactions. (A) The goal of a psychophysiological interaction (PPI) analysis is to explain the responses of one brain region (i.e., a target region) in terms of an interaction (gp × xA) between the influence of another brain region (i.e., a seed region; xA) and a particular psychological context (gp). There are two perspectives on PPIs. On the left, a PPI reflects a context‐specific change in effective connectivity between the two regions. In this case, the psychological context (e.g., attention) modulates the contribution of the seed region (region A) to the target region (region B). On the right, a PPI reflects a modulation of stimulus‐specific responses. In this case, the seed region (region A) modulates the response of the target region (region B) to the psychological context. [cf. Friston et al., 1997] (B) The usage of PPI in neuroimaging has increased rapidly since its inception. This popularity and widespread usage has led to a large corpus of PPI studies that can be probed using meta‐analytic techniques.
