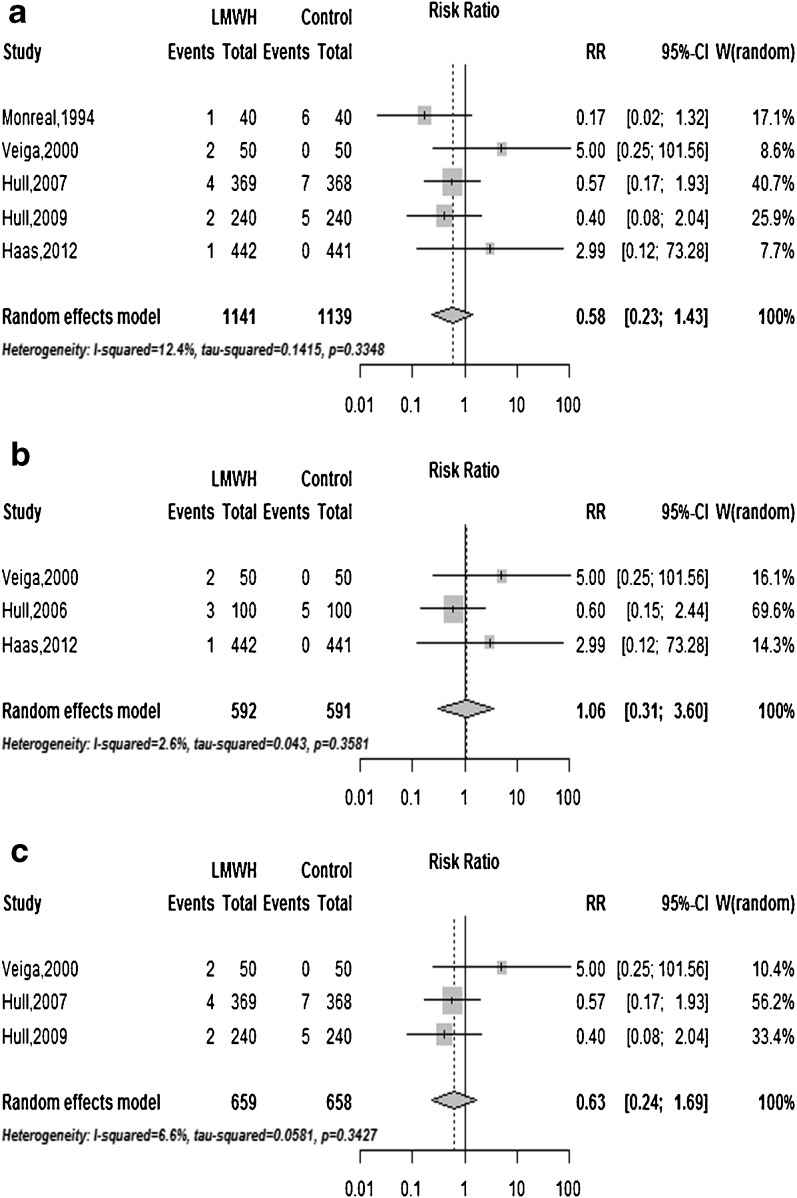
Figure 2.
a Forest plot: The effect of long-term low-molecular-weight heparin vs. control on all fractures in non-pregnant participants. LMWH denotes low-molecular-weight heparin. Control: unfractionated heparin, oral vitamin K antagonist or placebo; RR denotes risk ratio; RR < 1 favors LMWH; RR >1 favors control treatment. b Forest plot: Long-term low-molecular-weight heparin vs. control in cancer patients. LMWH denotes low-molecular-weight heparin. Control: oral vitamin K antagonist or placebo; RR denotes risk ratio; RR < 1 favors LMWH; RR >1 favors control treatment. c Forest plot: Long-term low-molecular- weight heparin vs. oral vitamin K antagonists in non-pregnant participants. LMWH denotes low-molecular-weight heparin. Control: oral vitamin K antagonists (i.e., acenocoumarol/warfarin); RR denotes risk ratio; RR < 1 favors LMWH; RR >1 favors control treatment.