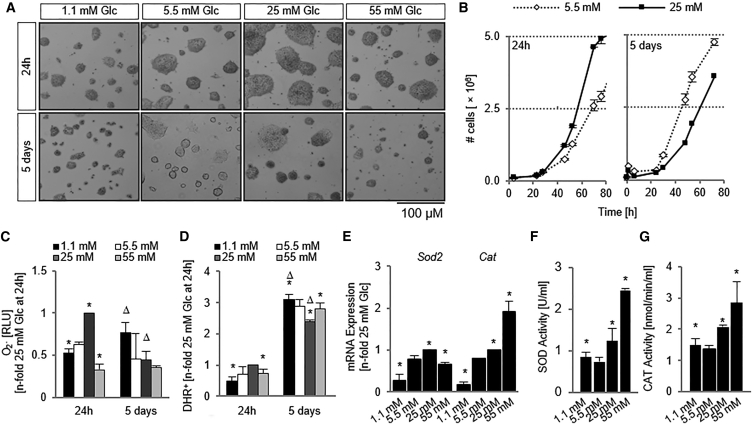
Figure 1.
Hyperglycemia Leads to a Decrease in Cell Number and Is Coupled with an Increase in Oxidative Stress
(A) Micrographs of D3 ESCs exposed to varying Glc concentrations.
(B) Cell counts demonstrated that brief hyperglycemic exposure led to an initial increase in cell numbers, but these numbers were decreased after 5 days of exposure. n = 3 independent replicates ± SD.
(C) Superoxide anion content normalized to cell number. n = 5 independent replicates ± SD.
(D) Percentage of cells positive for reacted dihydrorhodamine was recorded on a flow cytometer. n = 5 independent replicates ± SD.
(E) qPCR for the determination of Sod2 and Cat mRNA levels after 5 days of Glc exposure. n = 3 independent replicates ± SD.
(F) SOD activity was measured after 5 days and normalized to protein content. n = 5 independent replicates ± SD.
(G) CAT activity is also increased in a Glc-dependent manner. n = 5 independent replicates ± SD.
∗p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA versus 5.5 mM Glc at 24 hr; Δp < 0.05, one-way ANOVA versus 5.5 mM Glc at 5 days. Glc, glucose; SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; RLU, relative light units; DHR, dihydrorhodamine.