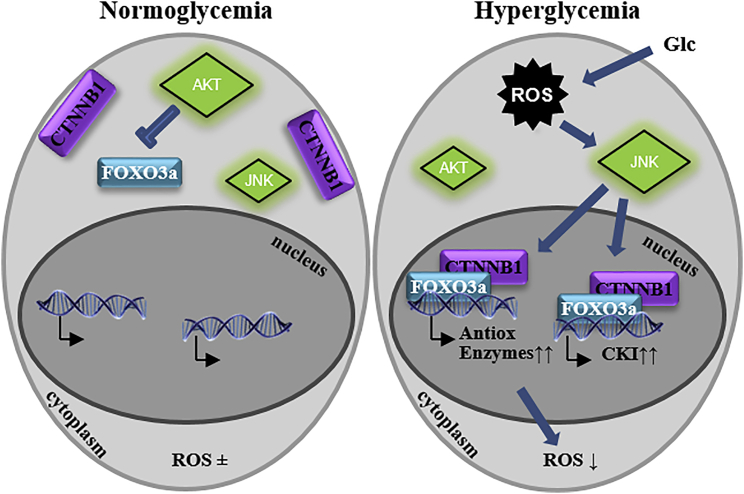
Figure 6.
Proposed Mechanism of Glc Action
Exposure to diabetic Glc leads to an immediate increase in ROS generation and subsequent JNK activation and results in the nuclear activation of FOXO3a/CTNNB1 by 5 days of exposure. This leads to the localization of this complex to the promoters of genes that regulate ROS removal and the cell cycle. In addition, AKT remains inactive in these conditions, rendering it unable to promote FOXO3a removal from the nucleus. CKI, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor; Glc, glucose; ROS, reactive oxygen species.