Figure 2.
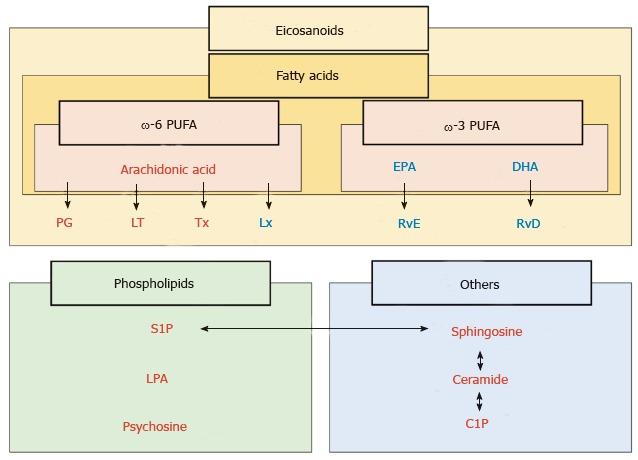
Classification of lipid mediators of inflammation. Lipid mediators are classified with fatty acids, phospholipids and others. Among the fatty acids, eicosanoids are the derivatives of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), which are present in dietary sources, such as fish oil (ω-3 PUFA) and vegetable oil (ω-6 PUFA). ω-6 PUFA generates prostaglandins (PG), leukotrienes (LT), thromboxanes (Tx) and lipoxins (Lx). Resolvin originates from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are components of ω-3 PUFA. Resolvin derived from EPA and DHA are termed resolvin E (RvE) and resolvin D (RvD) series, respectively, both of which act as pro-resolving mediators. Phospholipids including sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and others including ceramides and ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P) usually act as pro-inflammatory mediators. Red: Pro-inflammatory mediators; Blue: Pro-resolving mediators.
