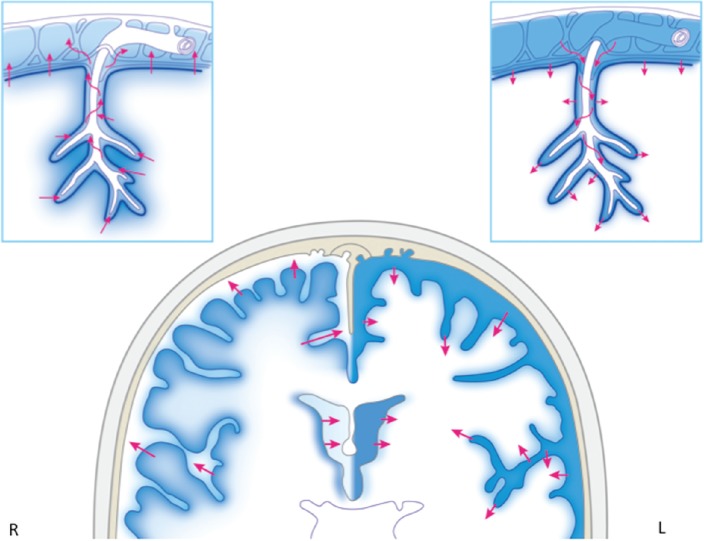
Fig. 6 .
A schematic diagram of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid exchange among the ventricle, subarachnoid space reservoir, and brain parenchyma is shown. Glia, which covers the neurovascular unit, is located at the border of the area in which water enters and exits the brain and spinal cord, and water is exchanged at the aquaporin channel of astrocyte foot processes or at other sites through the endothelium via diffusion or vesicular transport. Water movement at the ependymal layer, pia mater, and Virchow-Robin space is bidirectional. The right cerebral hemisphere has a mixing of interstitial fluid secreted within the brain parenchyma and CSF that enters the brain parenchyma, and subsequent drainage from the brain parenchyma into the CSF reservoir (subarachnoid space and ventricles). The left cerebral hemisphere shows that CSF penetrates from the ventricles and subarachnoid space into the brain parenchyma.