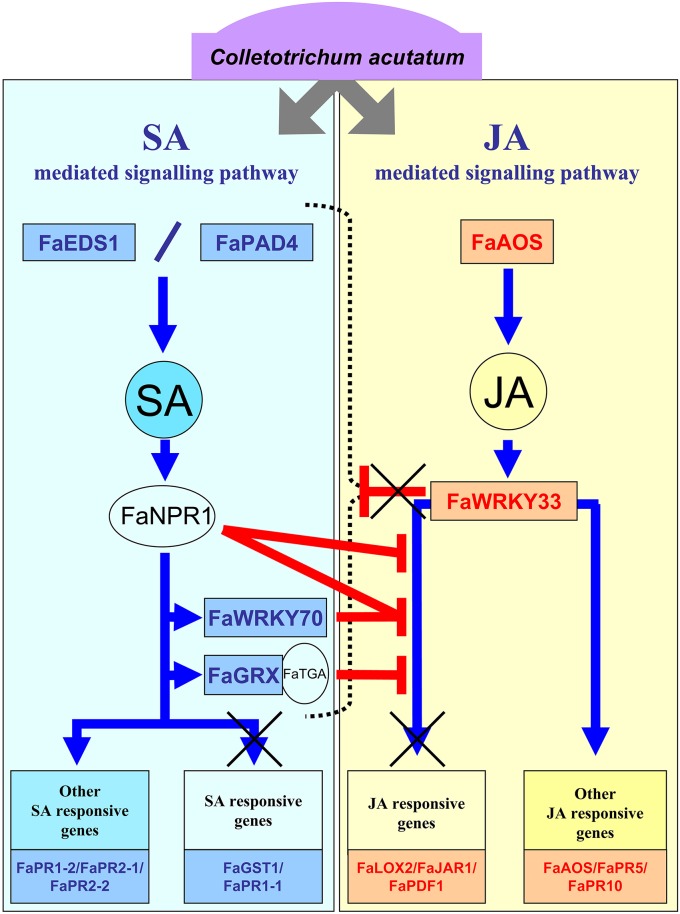
Figure 8.
Hypothetical model of SA- and JA-dependent defense pathways activated in strawberry in response to C. acutatum. This model is based on the canonical pathways described in model plant. Upon interaction with C. acutatum, the strawberry plant activates upstream components of SA and JA defense pathways. Thus, synthesis of these signal molecules increases and main downstream key components for SA (FaNPR1, FaWRKY70, FaGRX) and JA (FaWRKY33) are activated. Unlike Arabidopsis WRKY33, FaWRKY33 does not act as a negative regulator of the entire SA-dependent defense signaling pathway, either by a direct or an indirect effect of fungal activity, but only for some components (FaGST1, FaPR1.1). That allows FaGRX, together with FaNPR1 and FaWRKY70, to act as negative regulators of JA responsive genes similarly to their Arabidopsis orthologs. As a result, important JA-responsive defense marker genes, such as FaLOX2, FaJAR1, and FaPDF1, are not induced. These impaired mechanisms might provide some advantage for fungal spreading.