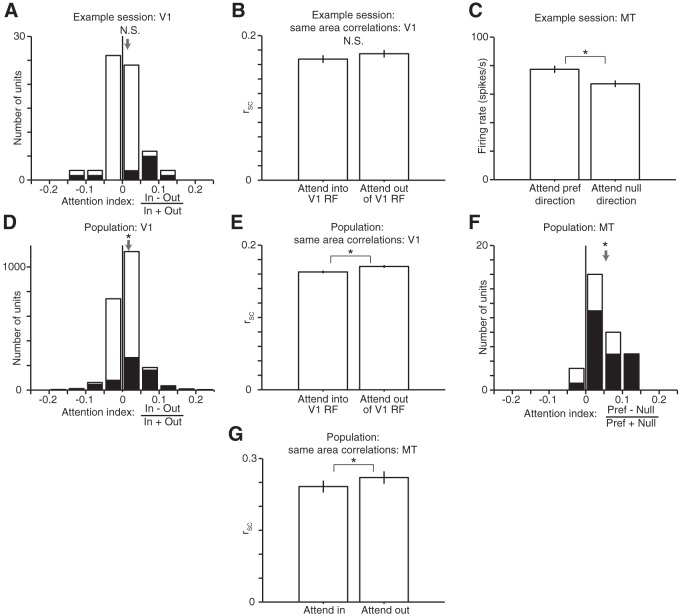
Figure 2.
Attention increases rates and decreases correlations in both V1 and MT. A, Histogram of attention indices for the V1 units from the example experimental session for which receptive fields are plotted in Figure 1B. The attention index quantifies attention-related changes in mean firing rate as the difference divided by the sum of the firing rates in the two attention conditions (62 units in this example session; the mean attention index = 0.008 is indicated by the gray arrow, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.097). Shaded bars indicate units with attention indices that differed from 0 (t tests, p < 0.05). B, Mean rSC between pairs of V1 units for the same example session in each attention condition. Attending to the joint receptive field of a pair of V1 units tended to decrease its spike count correlation (n = 1048 pairs, Wilcoxon ranked-sum test, p = 0.17). Error bars are ±1 SEM in all panels. C, Attention-related changes in firing rate for the MT unit recorded during the same example session. As was typical in our dataset, the firing rate was significantly higher when the animal attended to the stimulus moving at the unit's preferred direction (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, p = 0.007). D, Histogram of attention indices for 2178 V1 units across 42 recording sessions in two animals (mean attention index 0.011, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 5.5 × 10−47). Conventions as in A. E, Mean rSC between simultaneously recorded V1 units across all 34,404 pairs in 42 sessions in each attention condition. Attention significantly decreased rSC (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, p = 4.9 × 10−6). F, Histogram of attention indices for 32 MT units recorded in 32 recording sessions (one unit per session; mean attention index 0.05, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 3.5 × 10−6). Conventions as in A and D. G, Mean rSC between simultaneously recorded MT units in each spatial attention condition. These units were recorded on multielectrode probes in largely separate sets of experiments (n = 270 total pairs from 16 experimental sessions in Monkey 1 and 15 experimental sessions in Monkey 2; difference between attention conditions is statistically significant; Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.017).