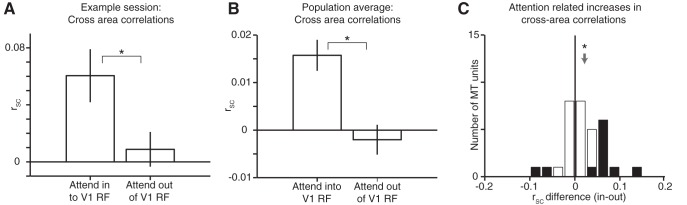
Figure 3.
Attention increases rSC between V1 and MT. A, Average cross-area rSC between V1 units and the MT unit from the same example experimental session in Figures 1B and 2A. We compared rSC on trials with full-contrast visual stimuli when the animal switched attention between the two stimuli inside the MT neuron's receptive field. Error bars represent ± SEM and the attention-related increase in rSC was statistically significant (62 V1–MT pairs, Wilcoxon ranked-sum test, p = 0.03). B, Average cross-area rSC between V1 units and the MT unit from all 1631 cross-area pairs across 32 recording sessions. Error bars represent ± SEM and the attention-related increase in rSC was statistically significant (Wilcoxon ranked-sum, p = 1.4 × 10−4). C, Histogram of average attention-related changes in cross-area rSC between each of 32 MT units and simultaneously recorded V1 units. The mean attention-related increase in rSC was significantly greater than 0 (mean = 0.018, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.029). Shaded bars indicate recording sessions for which the average attention-related change in cross-area rSC was significantly different from 0 (t test, p < 0.05).