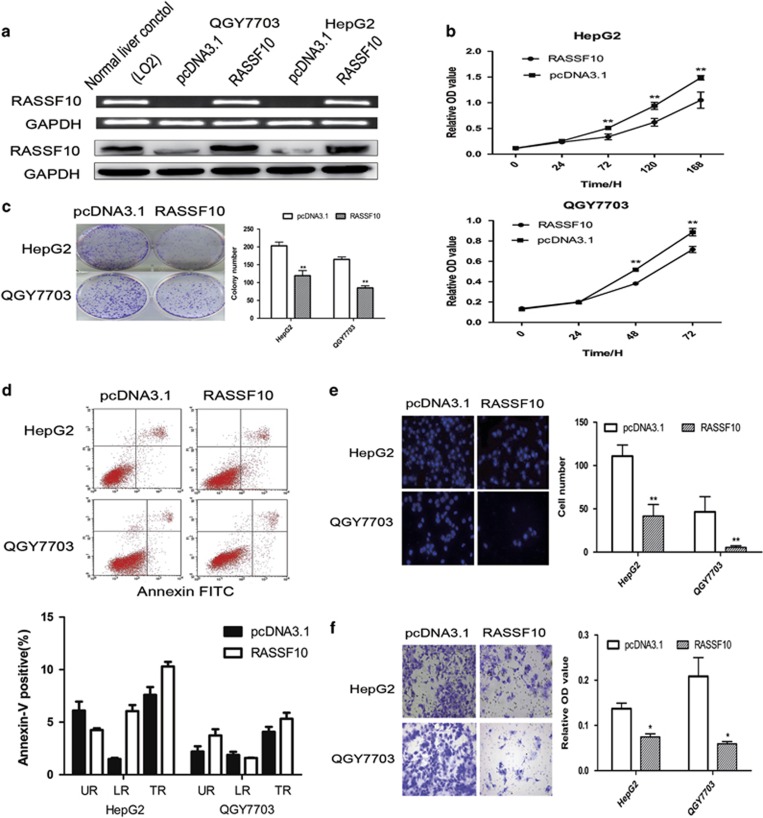
Figure 2.
RASSF10 inhibits HCC cell growth and cell invasion. (a) Restored expression of RASSF10 in QGY7703 and HepG2 cell lines was evidenced by RT-PCR and western blot. As compared with the normal liver control, no special higher levels of RASSF10 were observed in RASSF10-transfected HCC cells. GAPDH was used as internal controls. (b) RASSF10 significantly inhibited cell viability in HCC cell lines. (c) The monolayer colony formation assays. Left panel shows the representative images of the colony formation in HCC cell lines transfection with pcDNA3.1/RASSF10 or empty vector (pcDNA3.1). Quantitative analysis of colony numbers is shown in the right panel. (d) Effects of re-expression of RASSF10 on HCC cells apoptosis in HepG2 and QGY7703 cells. Apoptosis was not influenced by the restored expression of RASSF10, which was confirmed by FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection assay. Representative results of cell apoptosis were showed. (e) Cell migration assay was performed in modified Boyden transwell chambers assay. The migratory cells stained with DAPI display on the left panel. The mean number of visible cells was counted by fluorescence microscope in five random high power fields. (f) Cell invasion assay was used to assess cell invasion. Invaded cells were stained with cell stain solution, and then detected on a standard microplate reader (560 nm). All data represent the average of three independent experiments in duplicate. Data are mean±s.d. The asterisk indicates statistical significance (*P<0.05, **P<0.01).