Figure 1.
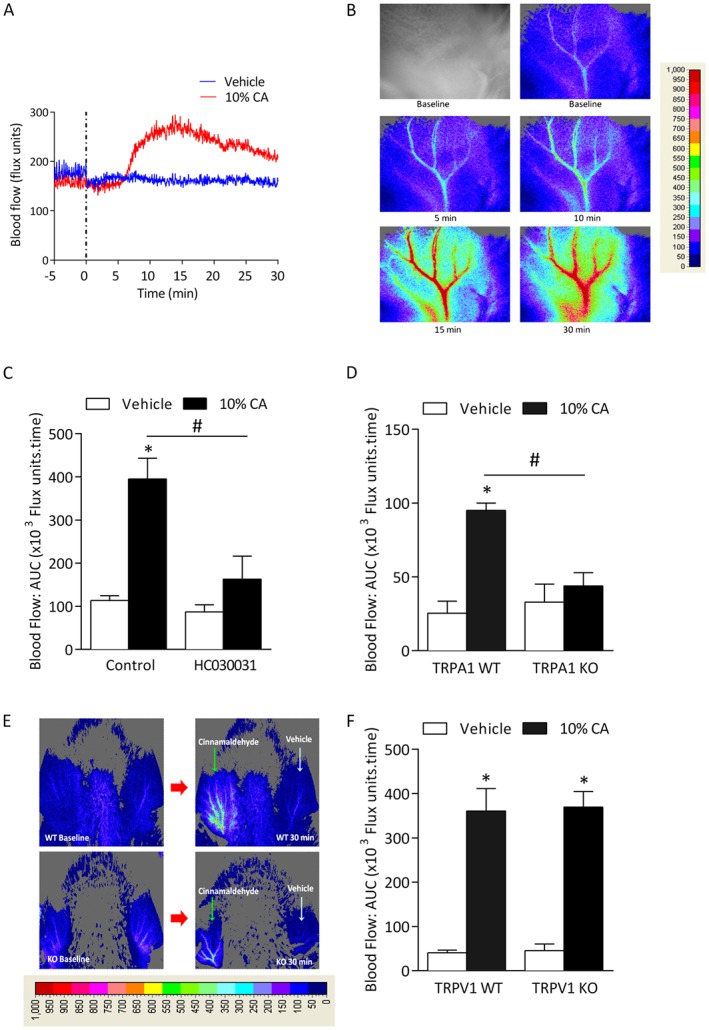
Cinnamaldehyde (CA)‐induced vasodilatation is dependent on TRPA1. Blood flow was measured in response to topical cinnamaldehyde (10% CA) and vehicle (10% DMSO in ethanol) in the anaesthetized mouse ear. Results recorded over 30 min and analysed as AUC. (A) Representative blood flow trace of CA‐induced response in WT mouse. Dotted lines represent topical administration of CA or vehicle. (B) Representative blood flow response as observed in pseudo‐colour images alongside grey/black image by laser speckle imager at baseline, 5‐30 min following treatment in WT mouse. (C) Group mean data for CA‐induced vasodilatation in WT mice pretreated with the TRPA1 antagonist HC030031 (100 mg·kg−1, n = 5) or control (10% DMSO in saline, n = 6). (D) Group mean data for CA‐induced vasodilatation in TRPA1 WT and KO mice (n = 5). (E) Representative blood flow response as observed in pseudo‐colour images by laser speckle imager at baseline and 30 min following treatment in TRPA1 WT and KO mouse. (F) Group mean data for CA‐induced vasodilatation in WT and TRPV1 KO mice (n = 5). All errors indicate SEM. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle‐treated ears of WT mice; #P < 0.05 versus CA‐treated ears of WT mice (2‐way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test).
