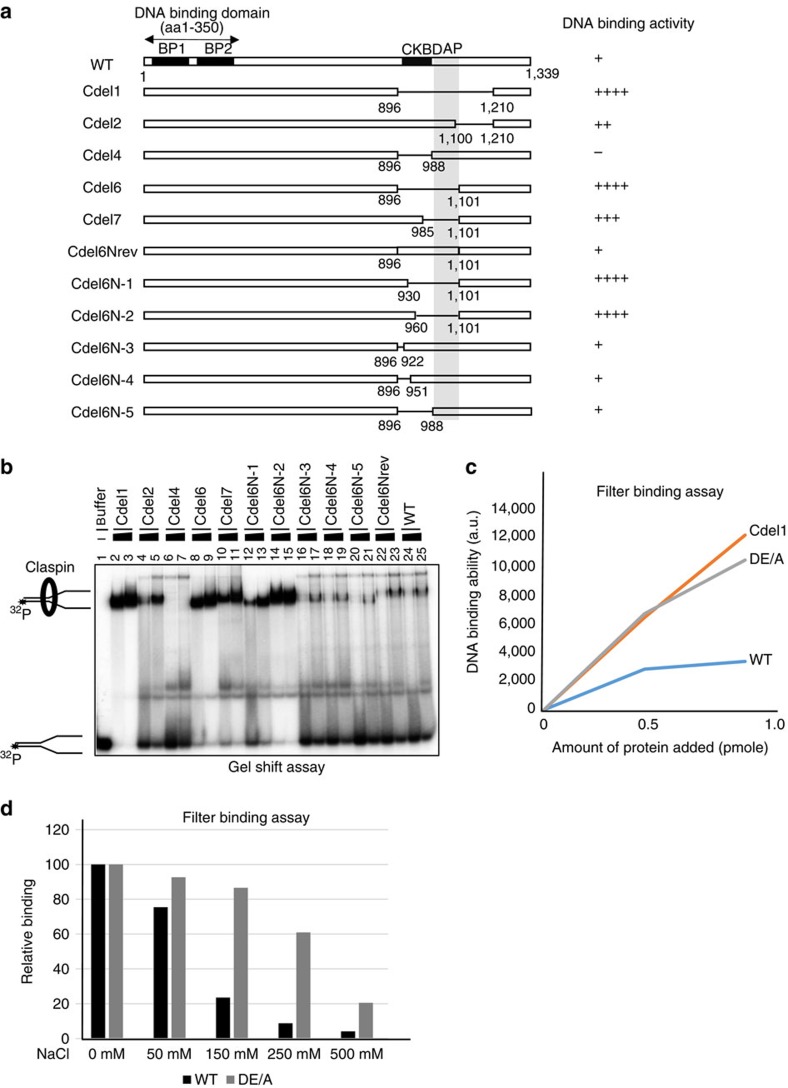
Figure 4. DNA-binding activity of Claspin is regulated by the C-terminal acidic patch.
(a) Schematic diagram of mutant Claspin-containing internal deletions within the C-terminal segment.+ Marks indicate the relative strength of DNA binding. BP1 and BP2, Basic patch1 and 2; CKBD, Chk1 binding domain; AP, acidic patch. The double arrowed segment (aa1–350) can bind to DNA with high affinity. (b) Gel shift assays of mutant Claspin proteins on Y-fork DNA. Y-fork DNA, 20 fmol; protein added, 0.5 and 1.0 pmol. The reason why Cdel4 fails to generate the larger protein–DNA complex is not clear. (c) Filter-binding assays of Cdel1 and DE/A mutant Claspin proteins on Y-fork DNA. Y-fork DNA, 80 fmol; protein added, 0.5 and 1.0 pmol. (d) Effect of salt on DNA binding activity of full-length and DE/A mutant Claspin proteins. Filter-binding assays were conducted as in c using the full-length and DE/A mutant Clapsin proteins (2 pmol), except that filters were further washed by binding buffer containing increased concentration of NaCl. Binding without additional wash was taken as 100.