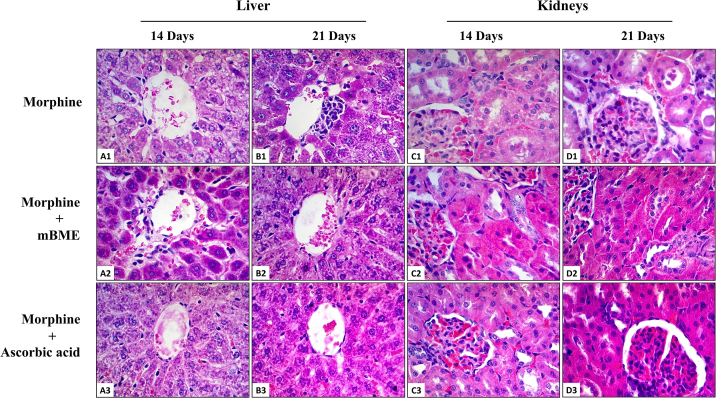
Fig. 2.
Histopathological evaluation of morphine induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity pretreated with mBME or ascorbic acid for 14 and 21 days (H & E; x400 original magnification) (n = 8 rats per group). (A1): Photomicrograph of a section of liver from a rat treated with morphine for 14 days showing dilatation of central vein and sinusoidal spaces, fatty accumulation, glycogen depletion and detachment of sinusoidal endothelial cells. (B1): Photomicrograph of a section of liver from a rat treated with morphine for 21 days showing central vein congestion, perivenular aggregation of lymphocytes, fatty accumulation, sinusoidal dilatation and infiltration of lymphocytes. Normal histology of central vein, hepatocytes and sinusoidal spaces were found in groups of rats treated with mBME (A2, B2) or ascorbic acid (A3, B3), two hours before administration of morphine for 14 and 21 days. (C1): Photomicrograph of a section of kidney from a rat treated with morphine for 14 days showing dilatation of renal tubules with cellular cast, proximal tubular epithelial cell vacuolization, increase amount of connective tissue in the glomerulus and interstitial fibrosis. (D1): Photomicrograph of a section of kidney from a rat treated with morphine for 21 days showing dilatation of renal tubules with cellular cast, interstitial fibrosis, congestion of glomerulus with red blood cells and an increase in the width of parietal layer of Bowman's capsule. Normal histology of renal corpuscle, proximal and distal convoluted tubules were found in groups of rats treated with mBME (C2, D2) or ascorbic acid (C3, D3), two hours before administration of morphine for 14 and 21 days.