Fig. 1.
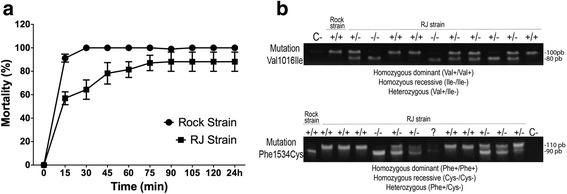
Characterization of pyrethroid resistance of two Ae. aegypti strains. a Five day-old Ae. aegypti female mosquitoes of the insecticide-susceptible ‘Rockefeller’ strain (Rock) and of the insecticide-resistant ‘Rio de Janeiro’ strain (RJ) were exposed to deltamethrin for up to 24 h and the percentage of mortality is shown. Data represent mean values of three experiments performed in triplicate ± standard deviation (SD). b Allele specific PCRs for genotyping kdr mutations were performed on adult Ae. aegypti mosquitoes from the RJ strain. Upper and lower panels represent reactions for the 1016 and 1534 mutation sites, respectively. In the upper panel, amplicons of approximately 80 and 100 bp correspond to alleles 1016 Val+ and 1016 Ile-, respectively. In the lower panel, amplicons of 90 and 110 bp correspond to alleles 1534 Phe+ and 1534 Cys-, respectively. Mosquitoes of the Rockefeller strain were used as positive homozygous dominant control for both mutation sites. C-: no template negative control
