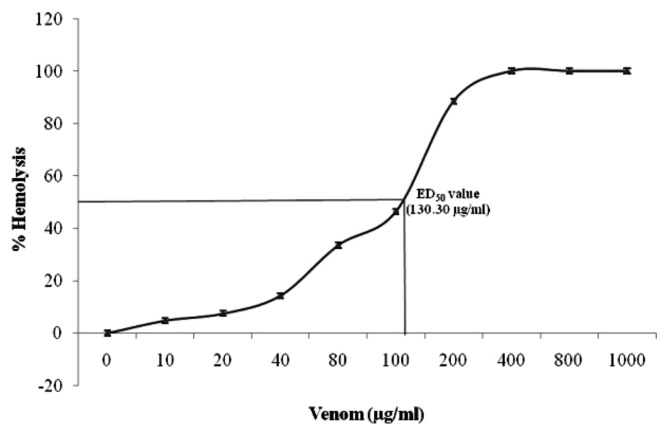
Fig. 1.
Hemolytic activity of A. stellatus toxin on human erythrocytes. Human erythrocytes were incubated with increasing doses of partially purified toxin for 60 min. Release of hemoglobin was determined by measuring the absorbance at 540 nm. Saline was used as a blank for the absorbance measurement. The 100% control for cell lysis was determined by addition of water values represent the mean ± SE of three experiments.