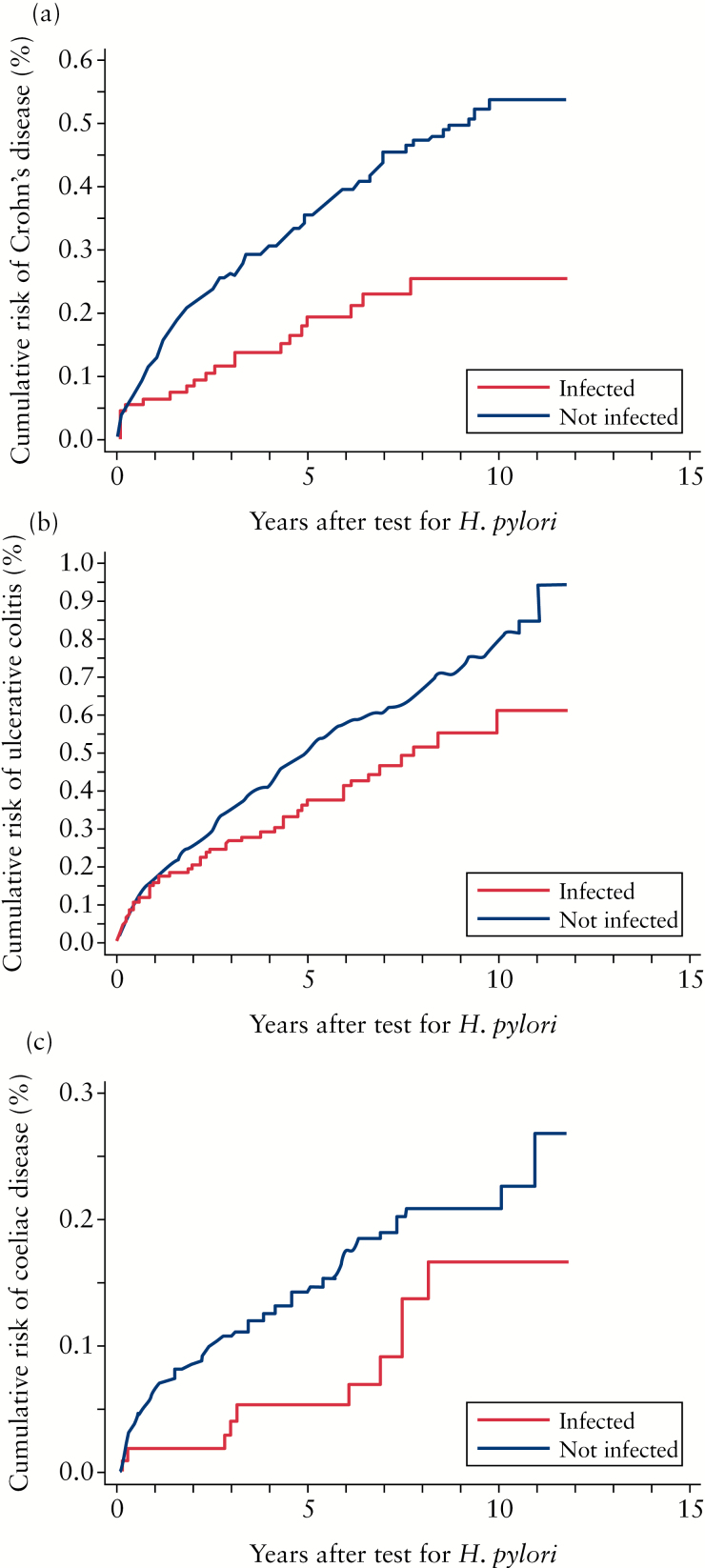
Figure 1.
Incidence of Crohn′s disease [CD], ulcerative colitis [UC], and coeliac disease [CeD] after urea breath test [UBT] with presumed Helicobacter pylori eradication after positive test. The dotted line represents patients who were H. pylori-negative by UBT, and the solid line represents patients who were H. pylori-positive by UBT. The x-axis shows time [years] whereas the y-axis shows cumulative risk [%, please note that the scale differs for the three diagnoses]. A: Cumulative risk of CD after UBT. A significantly increased incidence of CD was found in patients who were H. pylori-negative at UBT: hazard ratio 0.59 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.36–0.96). B: Cumulative risk of UC after UBT. A trend of an increased incidence of UC was found in patients who were H. pylori-negative by UBT: hazard ratio, 0.90 [95% CI: 0.64–1.27]. C: Cumulative risk of CeD after UBT. A trend of increased incidence of CeD was found in patients who were H. pylori-negative by UBT: hazard ratio 0.59 [95% CI: 0.29–1.22].