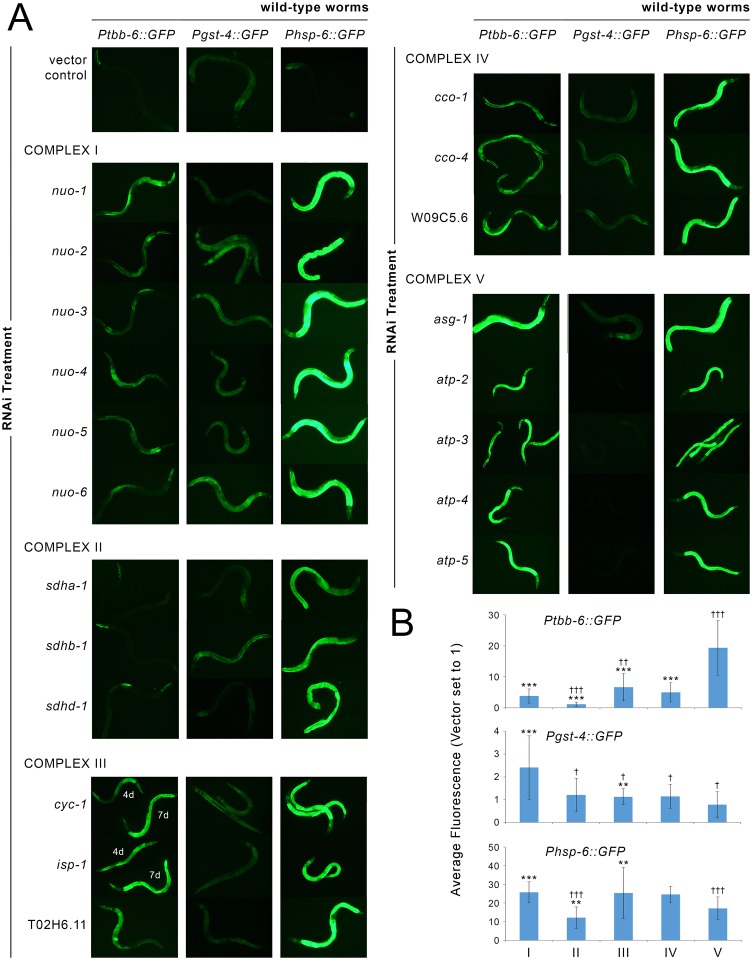
Fig 2. Ptbb-6::GFP reporter activation following mitochondrial ETC disruption.
(A) RNAi-mediated knockdown of mitochondrial respiratory chain subunits differentially induces Ptbb-6::GFP reporter expression relative to Pgst-4::GFP and Phsp-6::GFP. Shown are representative fluorescence images from a selection of subunits targeted in each complex. Quantified data of multiple replicates for all tested subunits is provided in S1–S3 Figs. (B) Mean change in GFP reporter fluorescence (+/-SD) when the effect of RNAi treatments targeting subunits from each ETC complex are averaged. Two statistical comparisons are shown (Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction applied for multiple comparisons): Asterisks indicate ETC complex disruptions which, on average, differ significantly in GFP fluorescence relative to knockdown of complex V subunits. Double daggers indicate ETC complex disruptions which, on average, differ significantly in GFP fluorescence relative to knockdown of complex I subunits. (*/†, p<0.01; **/††, p<0.001; ***/ǂǂǂ, p<0.00001) For complex III subunits cyc-1 and isp-1, 4d and 7d refer to 4 day—and 7-day old worms. For comparisons relative to empty vector see S4 Fig.