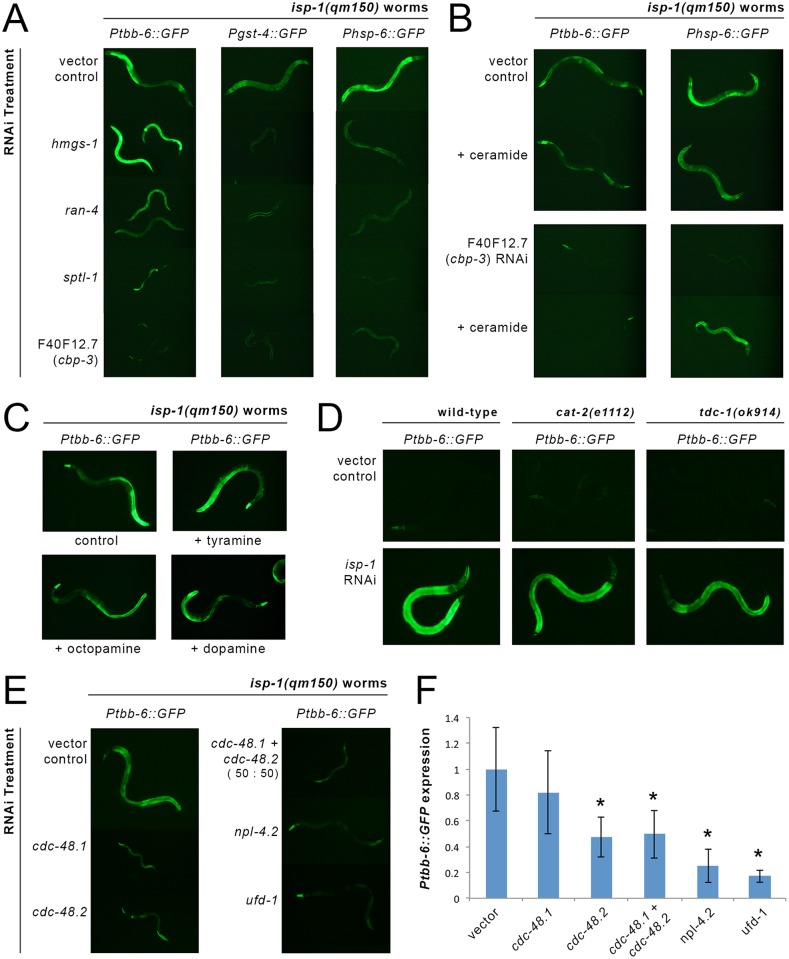
Fig 5. Ptbb-6::GFP marks a new cell surveillance pathway.
(A, B) Among genes known to function epistatically to atfs-1 in its role in activating the UPRmt [26, 60], only F40F12.7/ cbp-3 is also required for Ptbb-6::GFP expression (A). The role of cbp-3 in the Ptbb-6::GFP pathway is distinct from its role in the UPRmt, since ceramide addition only replaces the requirement for cbp-3 in UPRmt activation (B). (C, D) Monoamine neurotransmission and neuromodulation are dispensable for Ptbb-6::GFP activation. Neither dietary supplementation of L-tyramine, octopamine or dopamine (C), nor genetic inactivation of catecholamine synthesis (D), alters Ptbb-6::GFP activation following mitochondrial ETC disruption. (E, F) RNAi-mediated inhibition of core MAD pathway genes strongly inhibit Ptbb-6::GFP induction by isp-1(qm150) worms. Quantitative fluorescence imaging data is provided in panel F. (n = 4–7 worms per condition; asterisks indicate significantly (p<0.025) different relative to vector-treated animals).