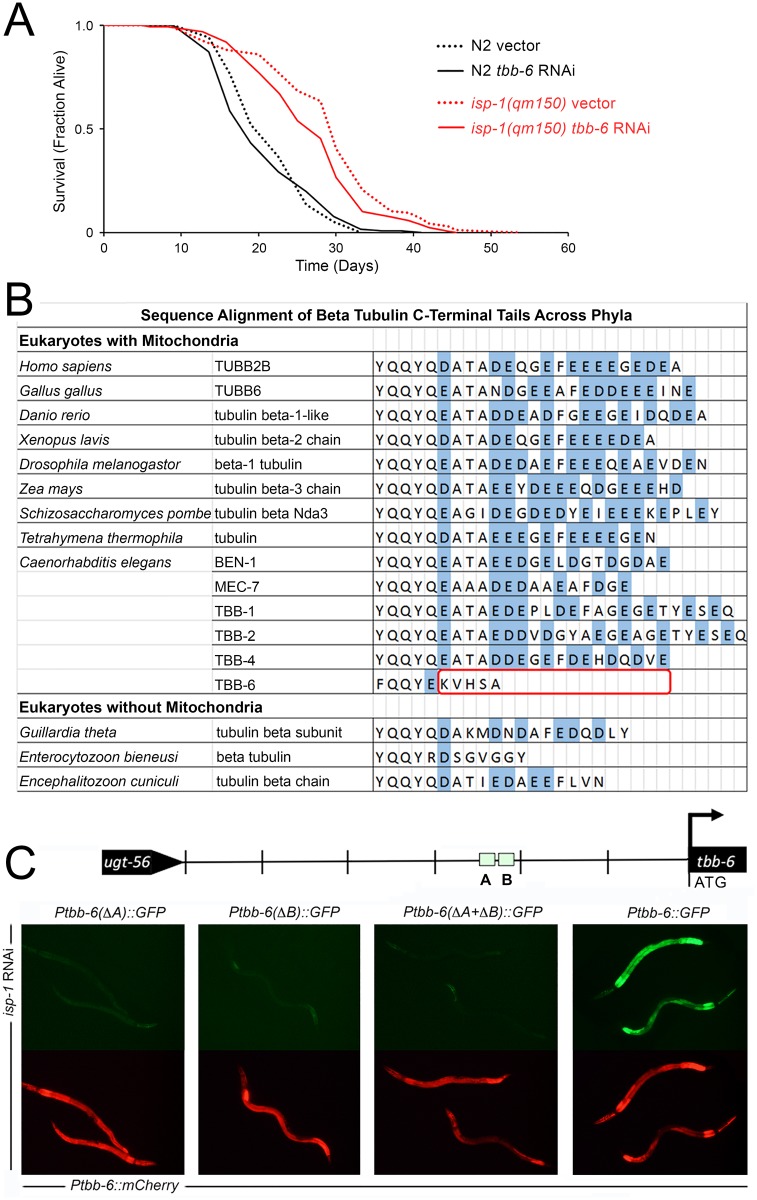
Fig 10. RNAi-mediated inhibition of tbb-6 mildly inhibits the life extension of isp-1(qm150) Mit mutants—potentially by mediating voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) activity.
(A) Survival analysis of isp-1(qm150) and wild type (N2) worms cultured on RNAi to tbb-6 or vector control (pL4440). The lifespan of isp-1(qm150) mutants is reduced by ~7% following knockdown of tbb-6. (Combined data from replicate experiments, Log rank test p < 0.003, N = 126–206 worms/condition). Full lifespan statistics in S4 Table. (B) C-termini of β-tubulins from various species. Non-C. elegans data derived from Fig 6A of Rostovtseva and colleagues [101]). (C) Removal of either of the two C/EBP-like motifs in the tbb-6 promoter of Ptbb-6::GFP abrogates GFP reporter expression. Transgenic lines contain mCherry under the control of the wild-type tbb-6 promoter as an internal control.