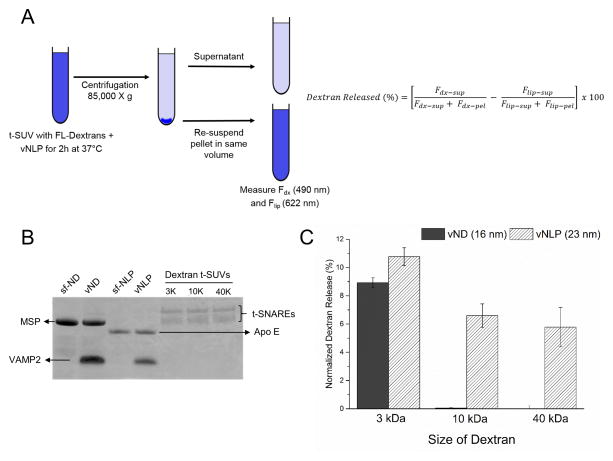
Figure 3.
NLPs accommodate the dilation of the fusion pore. (A) Schematics of the dextran release assay. Amount of encapsulated dextrans 3000 MW (stokes radius ~1 nm), 10,000 MW (~2.3 nm) and 40,000 MW (~4.4 nm) released in to the supernatant after fusion with vNLPs was estimated following pelleting of the vesicles. The dextran released (%) was corrected for inefficient pelleting and for non-specific leakiness/lysis. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis confirms that equal amounts of t-SNAREs have been incorporated in each dextran containing t-SUVs. The SNARE-free and VAMP2 (9 copies) containing ND and NLP used in this analysis are also shown (C) Normalized dextran released in the medium shows that dextrans of all sizes are efficiently released with NLPs as compared to the NDs confirming that NLPs accommodate expansion of the nucleated fusion pore up to at least ~9 nm