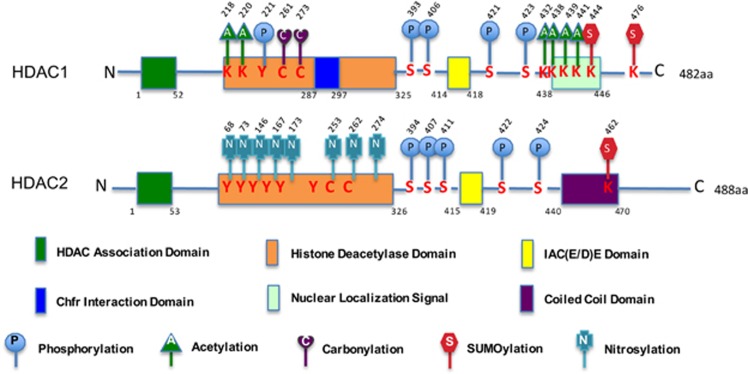
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of mammalian HDAC1 and HDAC2 structures with functional domains and post-translational modifications. HDAC1 and HDAC2 share a highly conserved N-terminal HDAC association domain (HAD) that is essential for homo- and hetero-dimerization. The C-terminal part contains an IAC(E/D)E motif (IACEE in HDAC1 and IACDE in HDAC2) involved in the interaction with the pocket proteins. HDAC1 has a 2-residue Chfr interaction domain and a nuclear localization signal (NLS) at the C terminus. HDAC2 contains a coiled-coil domain at the C terminus. HDAC1 and HDAC2 are regulated by different post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, nitrosylation, carbonylation, and sumoylation. K, lysine; C, cysteine; S, Serine; Y, tyrosine. Numbers indicate the corresponding amino-acidic (aa) position