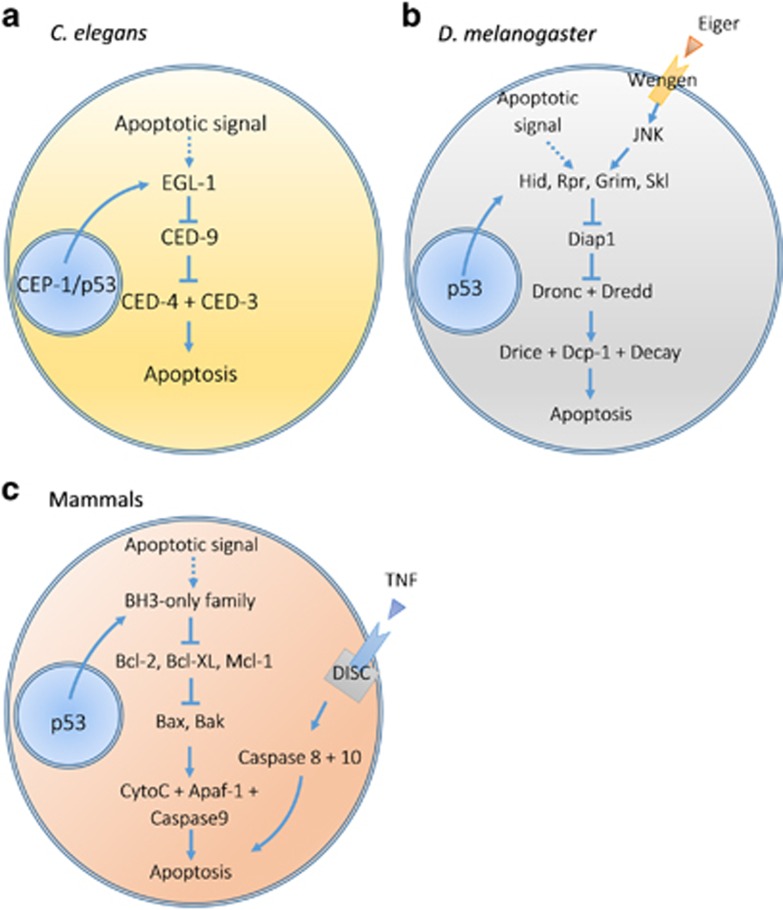
Figure 1.
Apoptosis pathways in various organisms. (a) In C. elegans, a stimulus (e.g. CEP-1/p53 in response to DNA damage) activates the core apoptosis pathway through transcriptional induction of EGL-1, leading to a suppression of CED-9. Suppression of CED-9 results in the release of CED-3 and formation of a complex with CED-4. This complex leads to apoptosis. (b) Apoptosis in D. melanogaster can be initiated autonomously or through receptor-mediated pathways. Activation of antagonists of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) including Hid, Rpr, Grim or Skl leads to inhibition of Diap1. Consequently, initiator caspases (Dronc and Dredd) are activated and lead to activation of effector caspases (Drice, Dcp-1 and Decay) and apoptosis. This pathway can be influenced by extrinsic factors including Eiger, upstream of JNK. (c). In mammals, apoptosis can be initiated intrinsically or extrinsically. The intrinsic pathway is similar to C. elegans and D. melanogaster pathways. In the extrinsic pathway, activation of a ‘death' receptor leads to formation of the death-inducing signalling complex (DISC) and activation of caspases 8 and 10, leading to apoptosis