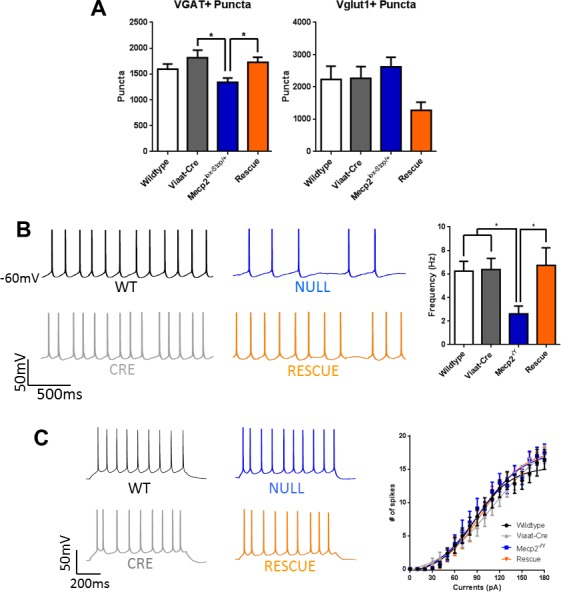
Figure 5. Inhibitory signaling in rescue mice showed some improvement while excitatory signaling was unchanged.
(A–B) Sample traces of mIPSC (A, Wildtype = 11, Viaat-Cre = 17, Mecp2lox-STOP/Y = 14, Rescue = 11) and mEPSC (B, Wildtype = 17, Viaat-Cre = 16, Mecp2lox-STOP/Y = 18, Rescue = 17) from pyramidal cells of the somatosensory cortex of wildtype, Viaat-Cre, Mecp2lox-STOP/Y, and Rescue male mice, including cumulative distributions of amplitude and interval, grand average minis, and summaries of frequency, amplitude, decay, and average charge. Error bars show SEM. *p<0.05
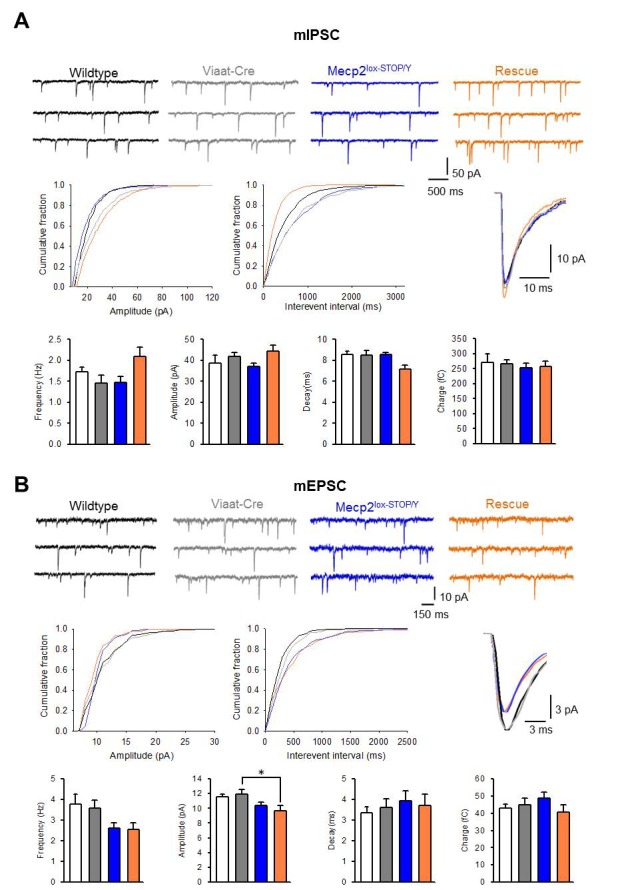
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Inhibitory synapse numbers and spontaneous action potential firing are normalized in rescue mice.