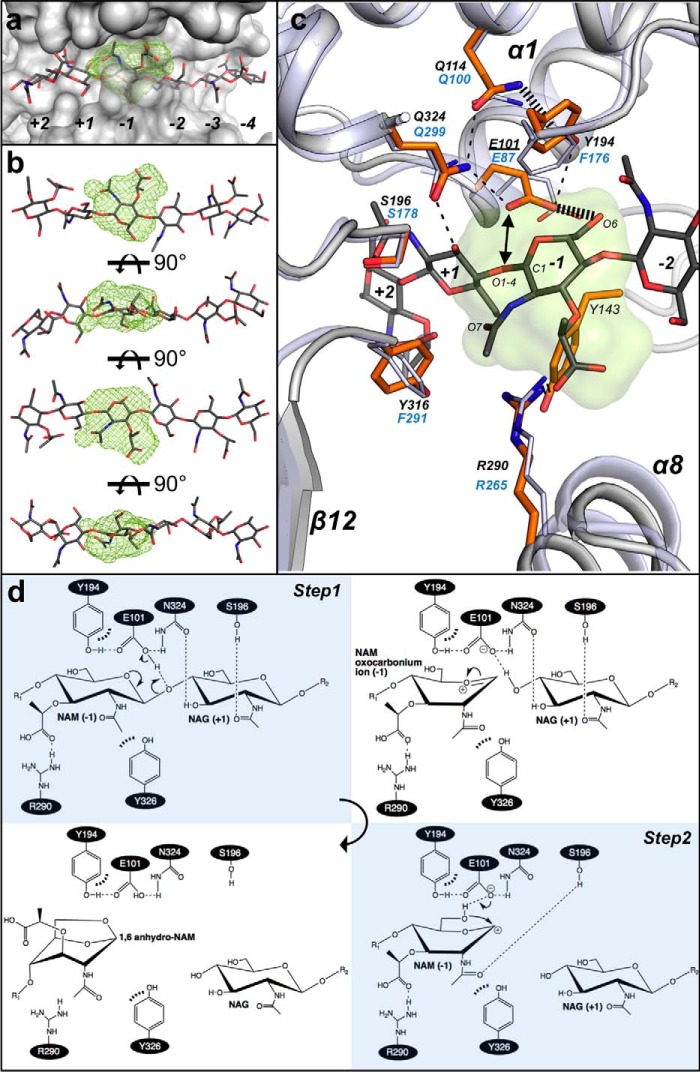
FIGURE 8.
Subsite −1 of SpoIID and the enzyme's catalytic mechanism. a, MIF (21) in lime green calculated by the analysis of the biochemical properties of the binding site identifies the location for favorable interaction clusters in the subsite −1 of CdSpoIID (white surface) and the (NAG-NAM)3 model. b, rotated views of (NAG-NAM)3 with NAM at subsite −1 fitted in the MIF (lime green). c, zoom-in of the subsite −1 of the superimposed CdSpoIID (white ribbon and orange sticks) and BaSpoIID (slate ribbon in transparence and slate sticks). (NAG-NAM)3 showed as dark gray sticks. The black dashes indicate hydrogen bond distances between atoms. d, mechanism of the reaction. In the first step, the catalytic glutamic acid donates its proton to the oxygen of the β1–4 bond, with the consequent formation of the oxocarbonium ion and release of the leaving group from the subsite +1 in the active site. In second step, the catalytic glutamate extracts the proton from the hydroxyl group at C6 of the NAM, allowing the intramolecular nucleophilic attack on C1 to form the 1–6-anhydro product (7).