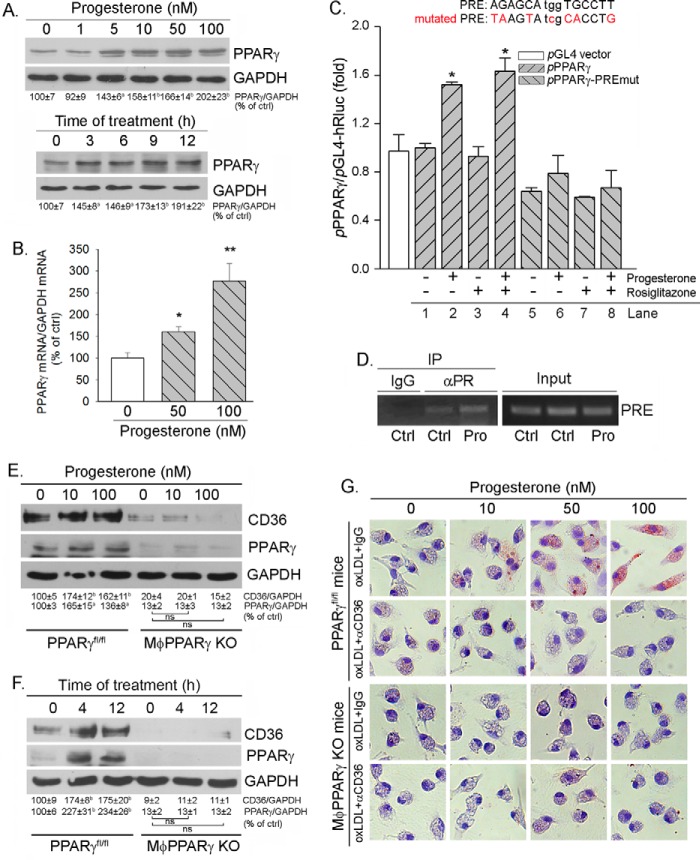
FIGURE 4.
Induction of CD36 expression by progesterone is completed by activating PPARγ expression. A and B, peritoneal macrophages isolated from female C57BL/6 wild-type mice were treated with progesterone at the indicated concentrations overnight or with 100 nm progesterone for the indicated times. Expression of PPARγ protein and mRNA was determined by Western blotting (A) and real time RT-PCR (B), respectively. a and *, p < 0.05; b and **, p < 0.01 versus control (ctrl) in the corresponding group (n = 3). C, J774 cells were transfected with DNA for pPPARγ or pPPARγ-PREmut plus Renilla, followed by treatment with progesterone, rosiglitazone, or both overnight. Total cellular lysate was extracted and used to determine firefly and Renilla luciferase activity. *, p < 0.05 versus pPPARγ alone (lane 1, n = 3). D, peritoneal macrophages isolated from female C57BL/6 wild-type mice were treated with 50 nm progesterone (Pro) overnight. Chromatin was then isolated from cells, followed by immunoprecipitation (IP) with normal IgG or anti-PR antibody as indicated. The PCR was conducted with the primers for the corresponding PRE in the PPARγ promoter. E and F, peritoneal macrophages were isolated from female PPARγfl/fl mice and MacPPARγ KO mice, respectively. The cells were treated with progesterone at the indicated concentrations overnight (E) or with 50 nm progesterone for the indicated times (F). After treatment, cellular proteins were extracted and used to determine CD36 and PPARγ protein expression by Western blotting. a, p < 0.05; b, p < 0.01 versus control; ns, not significantly different (n = 3). G, peritoneal macrophages isolated from female PPARγfl/fl and MφPPARγ KO mice were treated with progesterone at the indicated concentrations overnight. Cellular oxLDL accumulation was determined by Oil Red O staining.