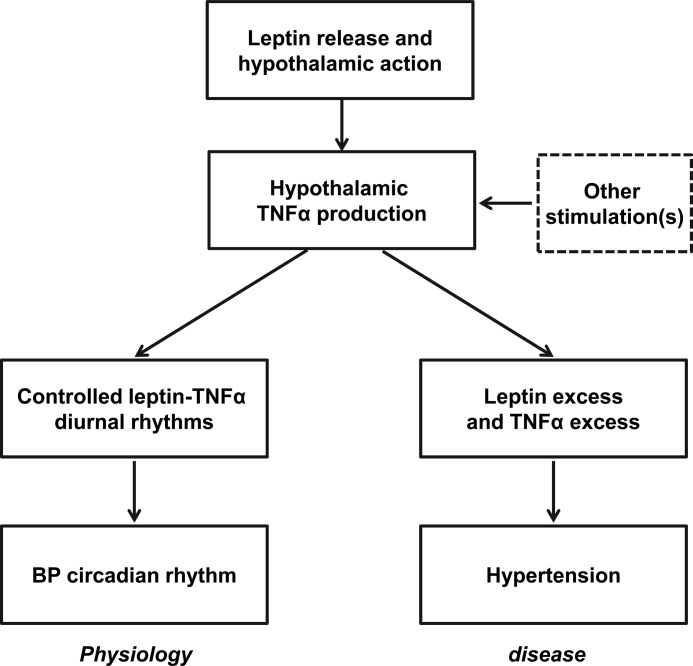
FIGURE 7.
Proposed model of central leptin and TNFα in BP control and hypertension. Increased leptin release can act in the brain to result in a controlled level of hypothalamic TNFα production, and through the central action of TNFα (which can also be contributed to by other factors in addition to leptin), it induces a moderate BP rise, which is physiologically associated with the active phase in diurnal cycles. Under conditions of obesity, which are prone to the development of hypertension, leptin, and TNFα are both chronically excess and thus induce an integrative action of chronically elevating BP, which can significantly contribute to the central mechanism of hypertension.